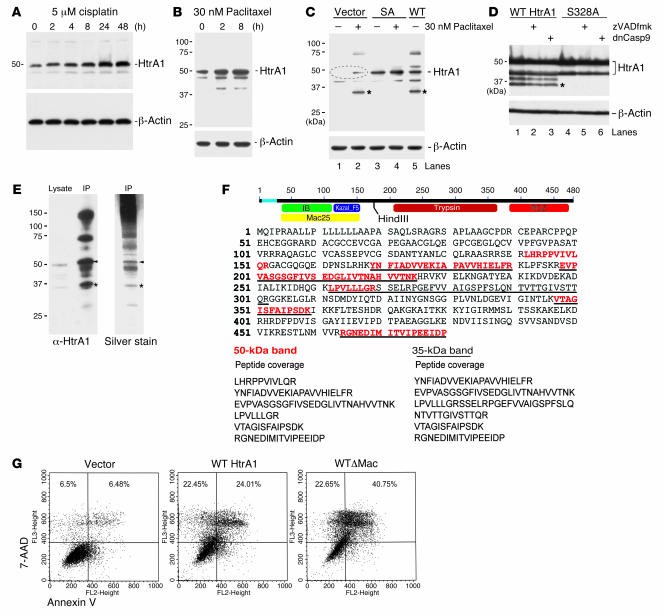
Figure 3. HtrA1 is upregulated and activated during chemotherapeutic drug treatment.
(A and B) SKOV3 cells were treated with cisplatin or paclitaxel, and lysates were taken at various time points. Immunoblot analysis of HtrA1 expression in these lysates (30 μg/lane) indicated upregulation of HtrA1 by cisplatin and paclitaxel. β-Actin immunoblots in the lower panels represent loading controls. (C) Immunoblot analysis of cells treated with paclitaxel for 24 hours indicated upregulation of HtrA1 (indicated by the dashed oval) and proteolysis of HtrA1 (35-kDa product in lane 2 indicated by an asterisk) that is dependent on HtrA1 protease activity, since protease mutant SA transfectants did not produce the smaller fragment in the presence of paclitaxel (lane 4). Forced expression of WT HtrA1 also produced a similar 35-kDa product (lane 5). (D) Pretreatment with 10 μM Z-VAD-FMK or cotransfection with dnCasp9 did not prevent proteolytic processing of HtrA1 (lanes 2 and 3). However, catalytic inactivation of HtrA1 (S328A) inhibited proteolysis of HtrA1 (lanes 4–6). Autocatalytic products are indicated by an asterisk. (E) To determine the domain composition of the 35-kDa product, it was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-HtrA1. Immunoblot and silver stain analyses detected 35-kDa and 50-kDa bands (indicated by asterisks and arrowheads, respectively). (F) LC-MS/MS analysis of the 35-kDa band showed peptide coverage missing in the Mac25 domain (underlined) but present in the 50-kDa band (red). (G) To compare the activities of 35-kDa and 50-kDa HtrA1, plasmid constructs (full-length and ΔMac25) were transfected into OV202 cells, and apoptotic activity was analyzed by annexin V labeling. Transfection of WTΔMac induced higher cell death compared with full-length HtrA1 (WT HtrA1).