Figure 6.
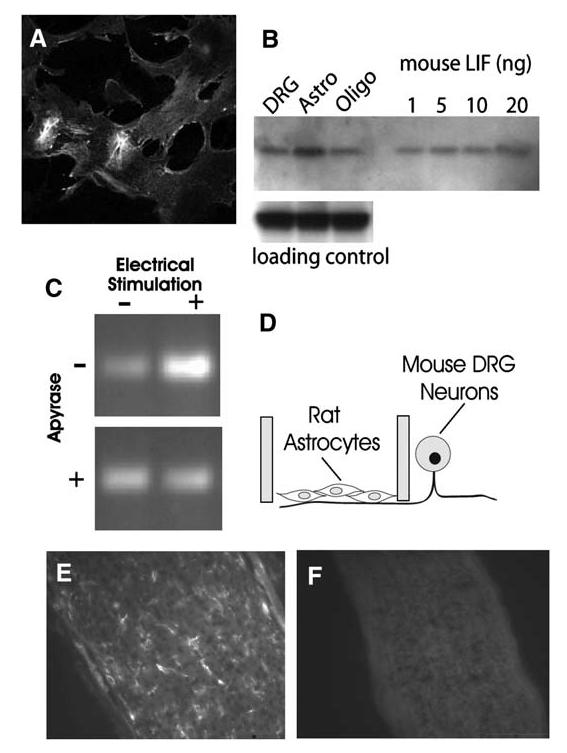
LIF Is Synthesized by Astrocytes and Regulated by Action Potential Firing(A) Astrocytes from E19 rat cortex stained strongly with anti-LIF antibody. DRG neurons and oligodendrocytes showed only weak staining with anti-LIF antibody, and astrocytes from LIF-/- mice were not stained (data not shown). (B) Western blot analysis confirmed the immunostaining results and indicated astrocytes as the predominant source of LIF in cocultures. (No microglia were detectable by immunocytochemistry.) Equal concentrations of protein (35 mg) from purified cultures of DRG neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes were compared. Antibody against ankyrin G was used as a control for equal loading in each lane. Purified mouse LIF confirmed the specificity of the LIF antibody and indicated that the amount of LIF in the astrocyte sample exceeds 20 ng. (C) The level of LIF mRNA in astrocytes grown on DRG axons was increased after 24 hr electrical stimulation of axons (top). This increase was prevented by stimulation in the presence of apyrase (30 U/ml), which degrades extracellular ATP (bottom). This indicates that the activity-dependent regulation of LIF mRNA levels in astrocytes occurs through a mechanism involving P2 purinergic receptor activation by ATP released from axons firing action potentials. (D) The experiments on effects of action potential firing on LIF mRNA in astrocytes were performed in multicompartment cell-culture chambers that separate the DRG cell bodies from axons. Astrocytes were derived from rats and plated onto mouse axons in the central compartment. Species-specific primers for LIF were used to ensure that the measurements did not derive from LIF mRNA possibly synthesized by neurons. As a control, PCR for 28s ribosomal RNA showed no change after any of the treatments in (C) (data not shown). (E) LIF is present in glia in vivo during the period of myelination in mouse optic nerve, as indicated by immunocytochemical staining of optic nerve from 10 day old mice. (F) Specificity of the antibody is shown by the lack of staining in LIF-/-mice.
