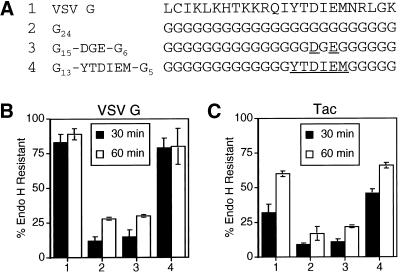
Figure 5.
Residues 19–24 of the VSV G tail are sufficient to mediate efficient ER export. (A) Amino acid sequence (single-letter code) of the C-terminal 24 residues of the cytoplasmic domain of the wild-type VSV G protein and poly-glycine mutant tails. Numbers to the left of the amino acid sequences refer to lane numbers in the graphs in B and C. Residues in the poly-glycine background that have been substituted with the wild-type VSV G sequence are underlined. BHK-21 cells expressing VSV G (B) or Tac (C) proteins containing the mutant tails described in A (with the additional sequence RVGIH or RIH, respectively, directly following the transmembrane domain) were pulse labeled for 5 min and chased for 30 or 60 min. Immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to endo H treatment as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS and separated by SDS-PAGE. The amount of endo H-resistant protein was quantitated by phosphorimaging. Each point represents the mean of a minimum of two experiments ± SD.