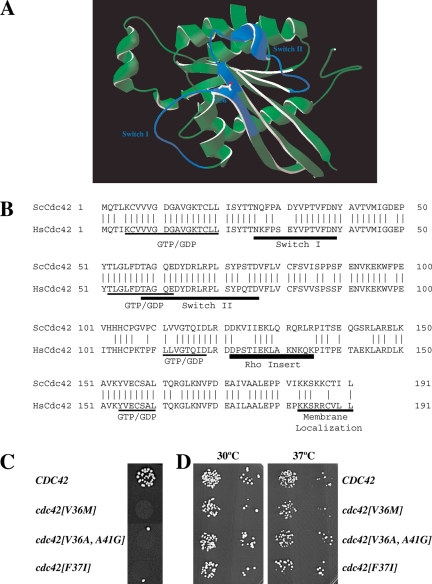
Figure 1.
Characterization of cdc42 mating mutants. (A) Three-dimensional structure model of S. cerevisiae Cdc42p. Model generated by homology modeling of S. cerevisiae primary sequence using Swiss-Model service based on the transition state Cdc42 complex for GTP hydrolysis structure pdb file 2NGR (Nassar et al., 1998). The amino acid residue Val 36 identified in this study is indicated, and Switch I and Switch II domains are colored in blue. (B) Sequence alignment of S. cerevisiae Cdc42p (ScCdc42) and human Cdc42 (HsCdc42). Vertical lines indicate identical residues. Guanine nucleotide-binding domain (GDP/GTP), Switch I and II regions, Rho insert, and membrane localization domain are indicated. (C) Spot mating of cdc42 mutants isolated from screen of aa 31-41. Matings using strains derived from RAY513 with indicated CDC42 or cdc42 gene (as sole copy behind its endogenous promoter on a CEN plasmid) are shown. Matings were carried out with the enfeebled tester RAY1142. (D) Cdc42 mutants grow normally. Serial dilutions of indicated mutants (same strains as above) were spotted onto YEPD plates and incubated for 2 d at the indicated temperatures.