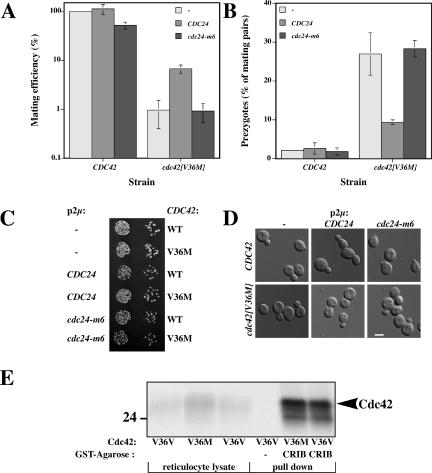
Figure 7.
Overexpression of CDC24 but not cdc24-m6 partially suppresses fusion defect in cdc42[V36M] matings. (A) Overexpression of CDC24 suppresses mating defect of cdc42[V36M] cells. Strains in which CDC42 or cdc42[V36M] is the sole copy behind its endogenous promoter on a CEN plasmid (derived from RAY1918 or RAY1920) and indicated CDC24 is overexpressed were analyzed for mating efficiency and prezygote formation as described in Figure 3, C and D. Values represent the means of two independent matings, with bars indicating actual values. Matings were carried out with the enfeebled tester JY429. (B) Overexpression of CDC24 suppresses the fusion defect of cdc42[V36M] cells during mating. Values represent the means of two independent matings (n = 200–300 mating pairs), with bars indicating actual values. (C) Overexpression of CDC24 and cdc24-m6 does not affect growth of cdc42[V36M] cells. Cells were spotted on −Ade plates as described in Figure 3A. (D) Overexpression of CDC24 or cdc24-m6 does not affect the morphology of cdc42[V36M] cells. DIC images of indicated cells used for above matings grown in −Ade-containing media. (E) Cdc42[V36M]p•GTPγS binds the Ste20p CRIB domain similar to wild-type Cdc42p. [35S]Cdc42p loaded with GTPγS was incubated with GSTCRIB immobilized on amylose resin and bound radioactivity was analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography. Input [35S]Cdc42p reticulocyte lysate (5%) is shown. Quantitation by phosphorimager revealed no difference between Cdc42p and Cdc42[V36M]p GSTCRIB binding, whereas binding of Cdc42[T35A]p was dramatically reduced (unpublished data).