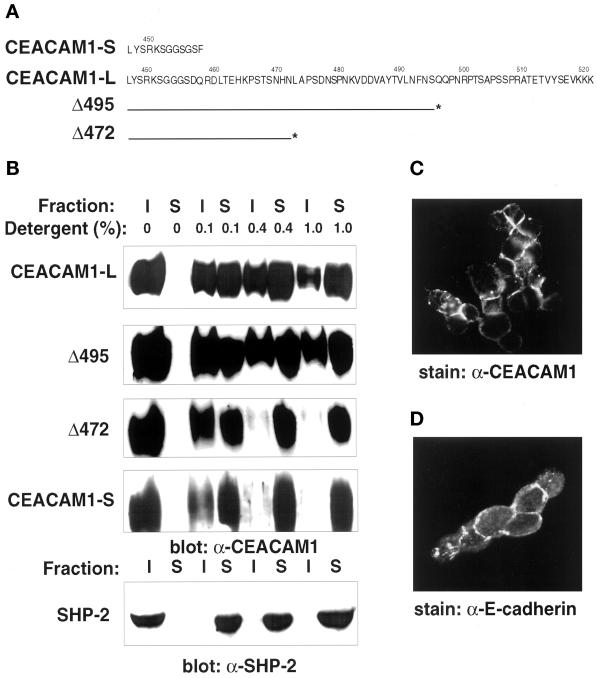
Figure 1.
Detergent solubility of CEACAM1 isoforms and deletion mutants. (A) The amino acid sequences of the short (CEACAM1-S) and long (CEACAM1-L) CEACAM1 cytoplasmic domains are presented in one-letter code. Numbers above the sequences indicate the positions in the full-length CEACAM1 protein. The lines below the CEACAM1-L sequence correspond to the C-terminal end of the protein in Δ495 and Δ472 CEACAM1-L deletion mutants. The asterisks correspond to the engineered stop codon. (B) CT51 mouse colon carcinoma cells stably expressing the CEACAM1 proteins were grown to ∼80% confluence and treated directly in the six-well dishes for 10 min at 4°C with buffers containing different concentrations of the Triton X-100 detergent (indicated above the lanes). Triton X-100 soluble (S) or insoluble (I) fractions were separated on 8% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to Immobilon membranes, and the presence of the CEACAM1 proteins was revealed using the 231 anti-CEACAM1 polyclonal antibody and an ECL detection system. The SHP-2 protein-Tyr phosphatase endogenously expressed in the CT51 cells was used as a control in these experiments. The cells were processed under identical conditions, and the protein was detected with an anti-SHP-2 polyclonal antibody raised against the C-terminal region of the protein. (C) Transfected CT51 cells stably expressing CEACAM1-L were subjected to treatment for 20 min at 4°C with a CSK buffer containing 0.5% Triton X-100 as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS. The cells were fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde and processed for indirect immunofluorescence using the CC1 anti-CEACAM1 mAb (C) or the anti-E-cadherin mAb (D).