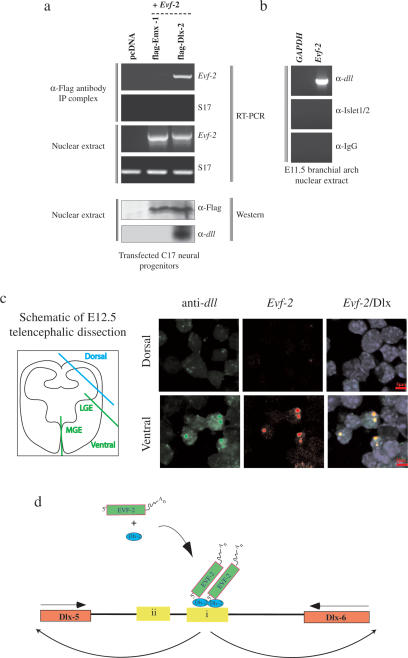
Figure 6.
Evf-2 and Dlx-2 form a complex in vivo. (a) Nuclear extracts made from C17 neural cells transfected with Flag-tagged Emx-1, Flag-tagged Dlx-2, or pcDNA control were analyzed for the presence of Evf-2–Dlx-2 complexes by immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody, followed by RT–PCR against Evf-2-specific primers and S17 control primers. Western analysis shows that both Flag-Emx-1 and Flag-Dlx-2 are present in nuclear extracts transfected with constructs expressing these proteins. (b) Nuclear extracts made from rat E11.5 BAs were analyzed for the presence of Evf-2/Dlx-2 complexes by immunoprecipitation with anti-dll, anti-Islet 1/2, or anti-IgG antibody, followed by RT–PCR against Evf-2-specific primers or GAPDH. (c) Single-cell suspensions made from mouse E12.5 dorsal and ventral telencephalon were dissected as shown in the schematic, centrifuged onto slides, and processed for fluorescent in situ/immunolocalization using Evf-2 antisense RNA probe and anti-dll antibody. DAPI staining (blue) reveals nuclei. Evf-2 RNA (Alexa fluor 568) is in red, Dlx (Alexa fluor 488) is in green, and regions of overlap are in yellow. (d) A model proposing that a complex of Evf-2 and Dlx-2 affects ei activity, ultimately affecting transcription of the Dlx-5 and Dlx-6 genes.