Figure 2.
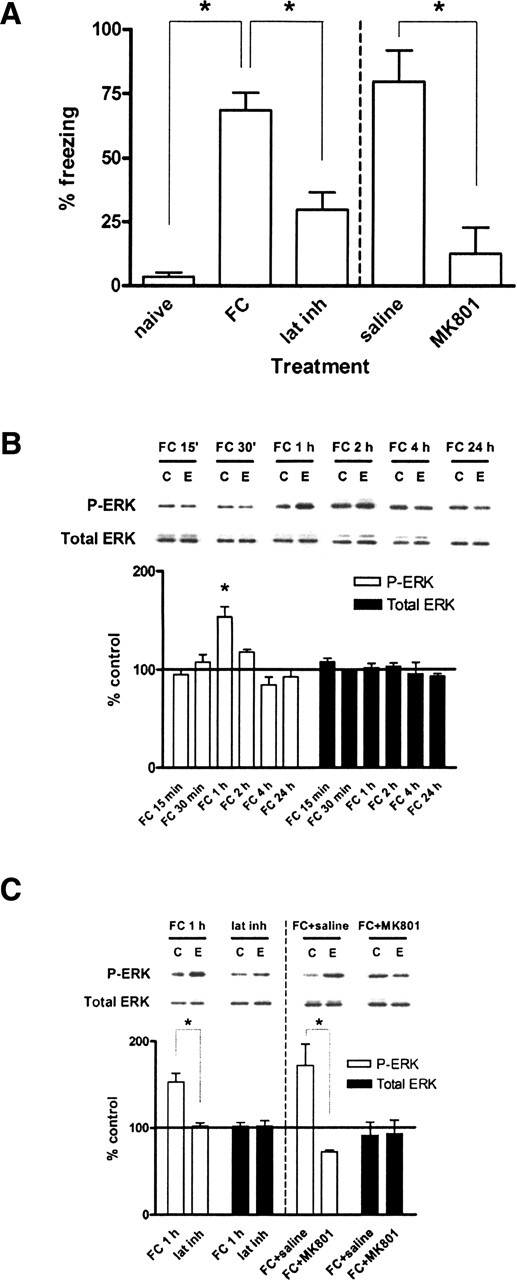
Contextual fear conditioning leads to formation of long-term fear memory and regulates ERK phosphorylation in vivo. (A) Quantification of freezing behavior 24 h following the training period. Animals trained under the contextual fear conditioning paradigm (FC, n = 12) displayed significantly greater freezing than either naive animals (naive, n = 4) or animals trained under the latent inhibition paradigm (lat inh, n = 12). Naive animals had not been previously exposed to either the training chamber or shocks. Animals injected with MK801 (300 μg/kg, n = 4) displayed significantly less freezing than animals injected with saline (0.9% NaCl, 1.25 mL/kg, n = 5). (B) Quantification of immunoblot densities for phospho-ERK and total ERK at different time points following contextual fear conditioning. ERK2 phosphorylation in area CA1 was significantly increased at 1 h after training (FC 1 h, n = 11) before returning to baseline and remaining even after 24 h. Total ERK was unchanged. Representative immunoblots for P-ERK and total ERK are shown for each time point. Control (C) samples appear on the left and experimental (E) samples appear on the right. (C) Quantification of immunoblot densities for phospho-ERK and total ERK. The latent inhibition paradigm (lat inh, n = 6) significantly reduced ERK2 phosphorylation in area CA1 compared with fear conditioning (FC 1 h, n = 11). Injection of animals with MK801 (300 μg/kg) prior to fear conditioning (FC + MK801, n = 3) significantly reduced ERK2 phosphorylation in area CA1 compared with injection with saline (0.9% NaCl, 1.25 mL/kg) prior to fear conditioning (FC + saline, n = 3). Total ERK was unchanged. Representative immunoblots for P-ERK and total ERK are shown for each condition. Control (C) samples appear on the left and experimental (E) samples appear on the right. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Asterisks denote significant differences (P < 0.05) as determined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
