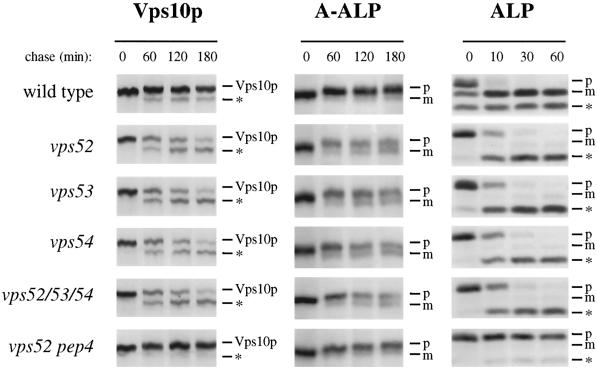
Figure 2.
Golgi membrane proteins undergo cleavage by vacuolar proteases in vps52, vps53, and vps54 mutants. (Left panels) Vacuolar cleavage of the CPY receptor Vps10p. Wild-type (SNY36-9B), vps52Δ::kanr (LCY222), vps53::Tn3URA (LCY221), vps54Δ::TRP1 (LCY200), vps52Δ::kanr vps53::Tn3URA vps54Δ::TRP1 (LCY280), and vps52Δ::kanr pep4Δ::LEU2 (LCY319) strains were radiolabeled for 10 min with [35S]methionine. After chasing for the indicated times, aliquots of cells were removed and subjected to immunoprecipitation with antibodies to Vps10p. Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and fluorography. The positions of full-length Vps10p and its PEP4-dependent cleavage product (*) are indicated. (Center panels) Processing of the late Golgi marker protein A-ALP. Strains containing a centromere-based plasmid encoding A-ALP (pSN55 for SNY36-9B, LCY280, LCY200, and LCY319; pSN246 for LCY221 and LCY280) were subjected to pulse-chase immunoprecipitation and analyzed as described above except that anti-ALP antibodies were added to immunoprecipitate A-ALP from the cell extracts. ProA-ALP (p) is converted to the faster-migrating mature form (m) by PEP4-dependent processing in the vacuole. (Right panels) Maturation of the vacuolar membrane protein ALP. Strains harboring plasmids for the expression of ALP (pSN92 for SNY36-9B, LCY280, LCY200, and LCY319; pNB6 for LCY221 and LCY280) were pulse chased for the indicated times, immunoprecipitated with anti-ALP antibodies, and analyzed as described above. PEP4-dependent cleavage of proALP (p) results in the formation of the mature form (m) as well as an additional commonly observed degradation product (*).