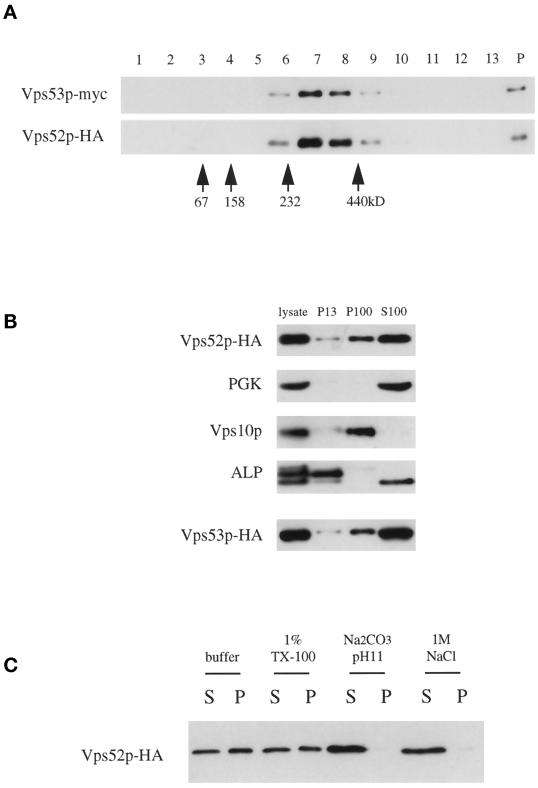
Figure 9.
(A) Vps52p and Vps53p cosediment on sucrose velocity gradients. The low-speed supernatant from LCY227 cells lysed in buffer containing 1% Triton X-100 was loaded at the top of a continuous 10–30% sucrose gradient and spun for 4.5 h, and a mixture of molecular mass markers was run in parallel on a second gradient. Three percent of each fraction, collected from the top of the gradient (lanes 1–13), as well as 10% of the material that sedimented to the bottom of the tube (lane P), was analyzed by Western blotting for myc and HA epitopes. The positions of the molecular mass markers (determined by Coomassie staining of SDS-PAGE gels) are indicated. (B) Association of Vps52p-HA and Vps53p-HA with the high-speed pellet. Subcellular fractions were prepared from a vps52Δ strain containing pLC72 (Vps52p-HA) by differential sedimentation as described in MATERIALS AND METHODS, separated by SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by Western blotting for HA, phosphoglycerate kinase (cytosolic marker protein), Vps10p (Golgi marker), and ALP (vacuolar marker; the faster-migrating band present in the S100 is a soluble degradation product). Subcellular fractions were prepared in parallel from a vps53::Tn3 strain containing pLC75 (Vps53p-HA) and analyzed by blotting for the same markers; only the anti-HA blot is shown. (C) Vps52p is peripherally associated with P100 membranes. S13 supernatant fractions from LCY226 were treated with 1% Triton X-100 (TX-100), 0.1 M Na2CO3, pH 11, or 1 M NaCl for 10 min at 4°C before centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 45 min. Equal amounts of the supernatant (S) and pellet (P) were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-HA antibodies.