Abstract
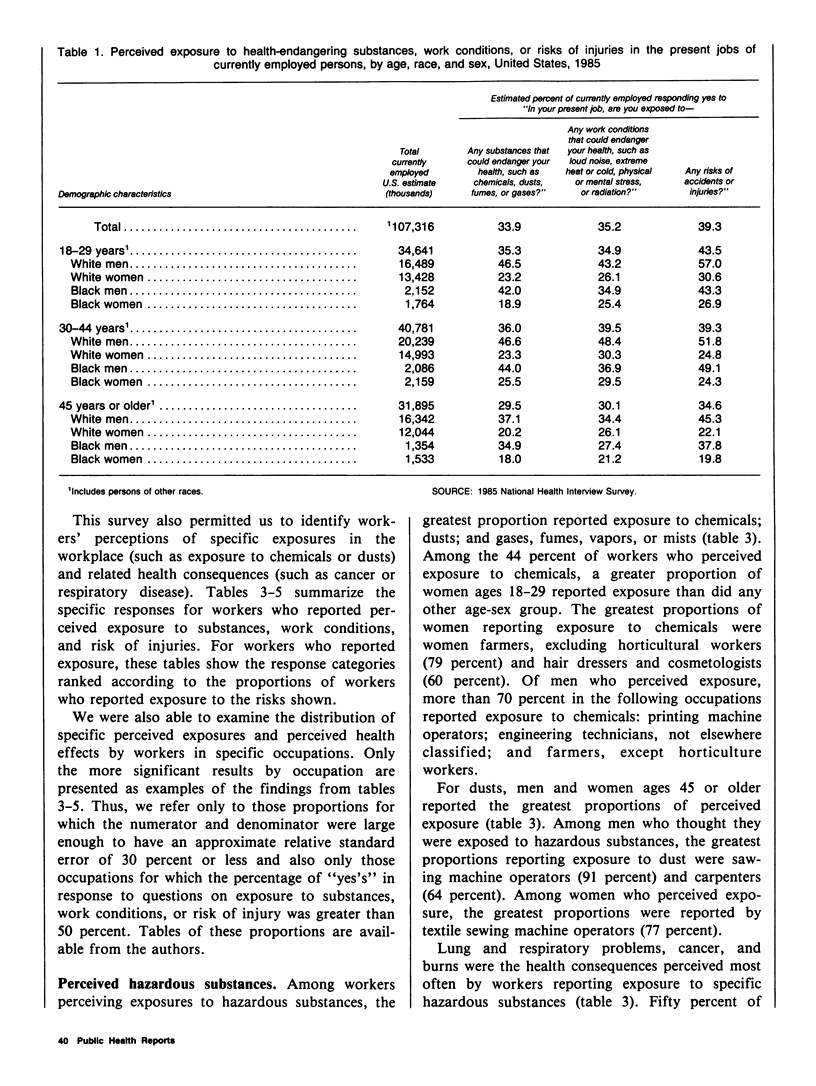
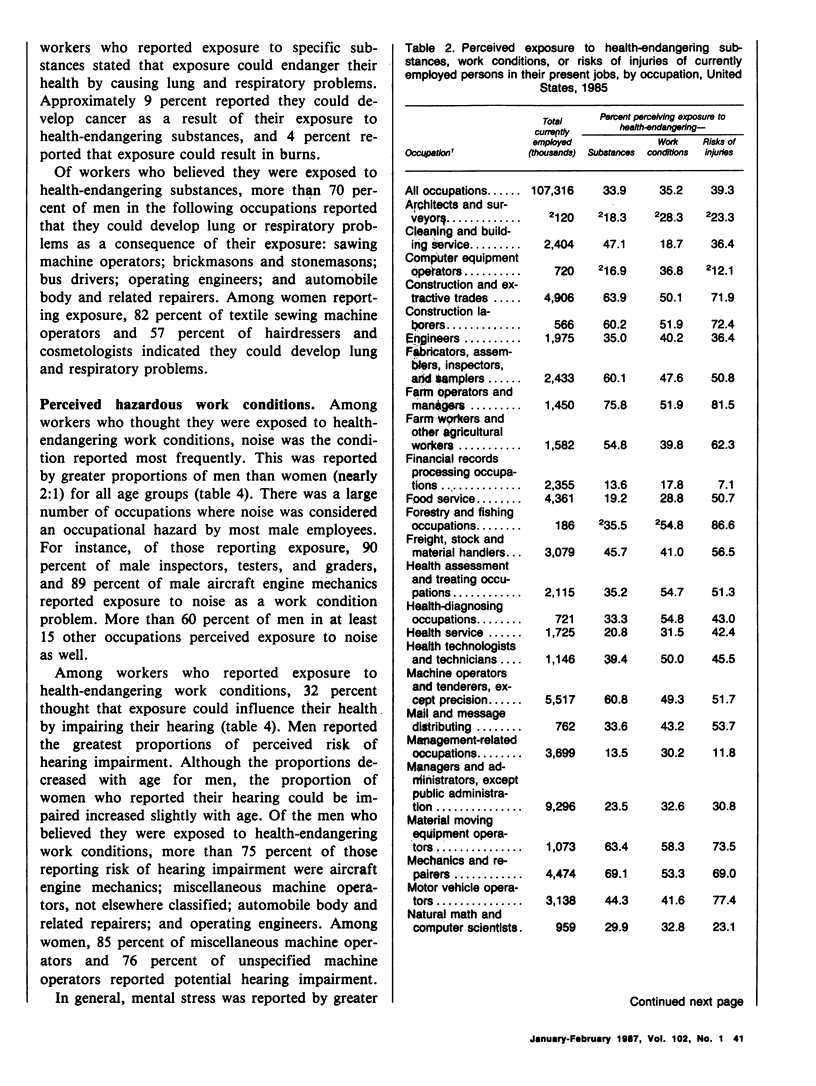
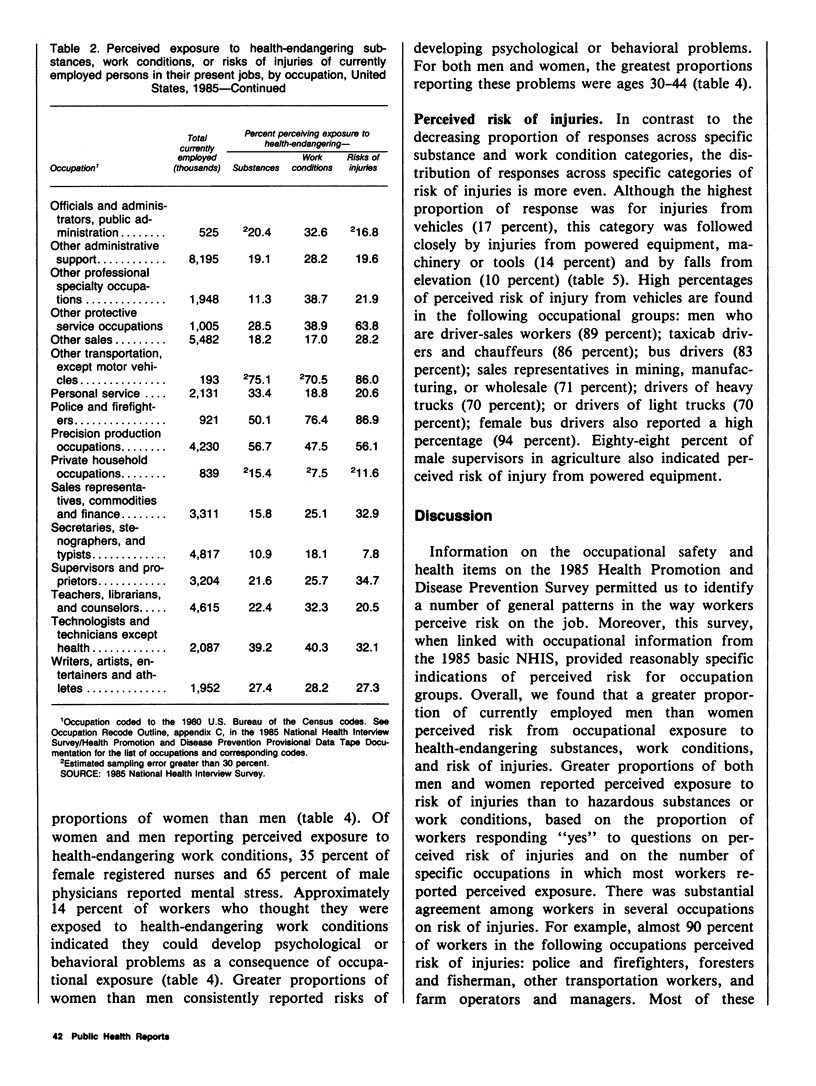
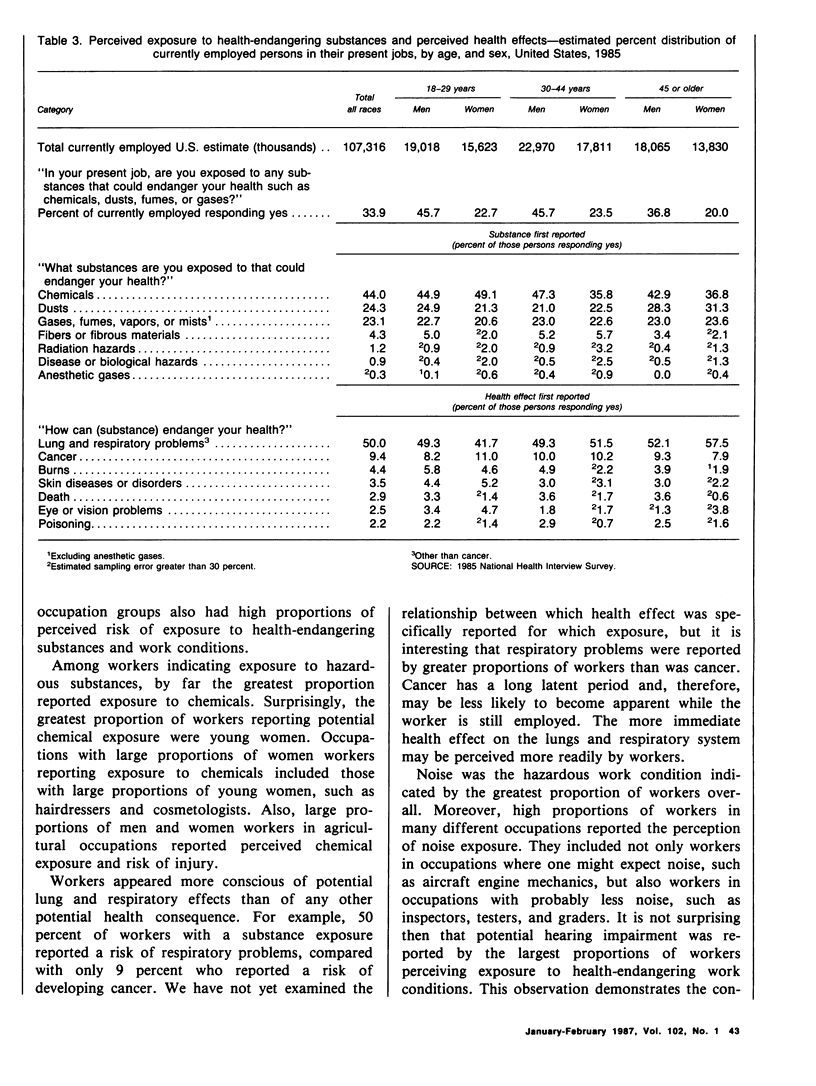
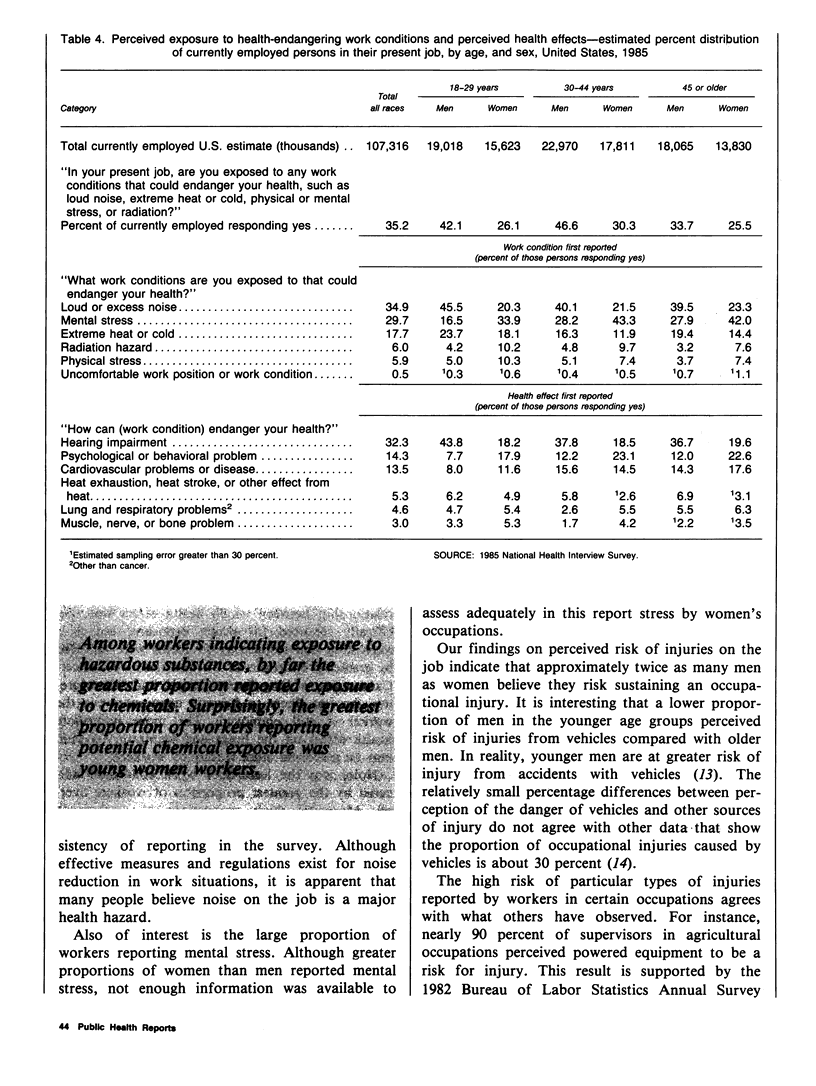
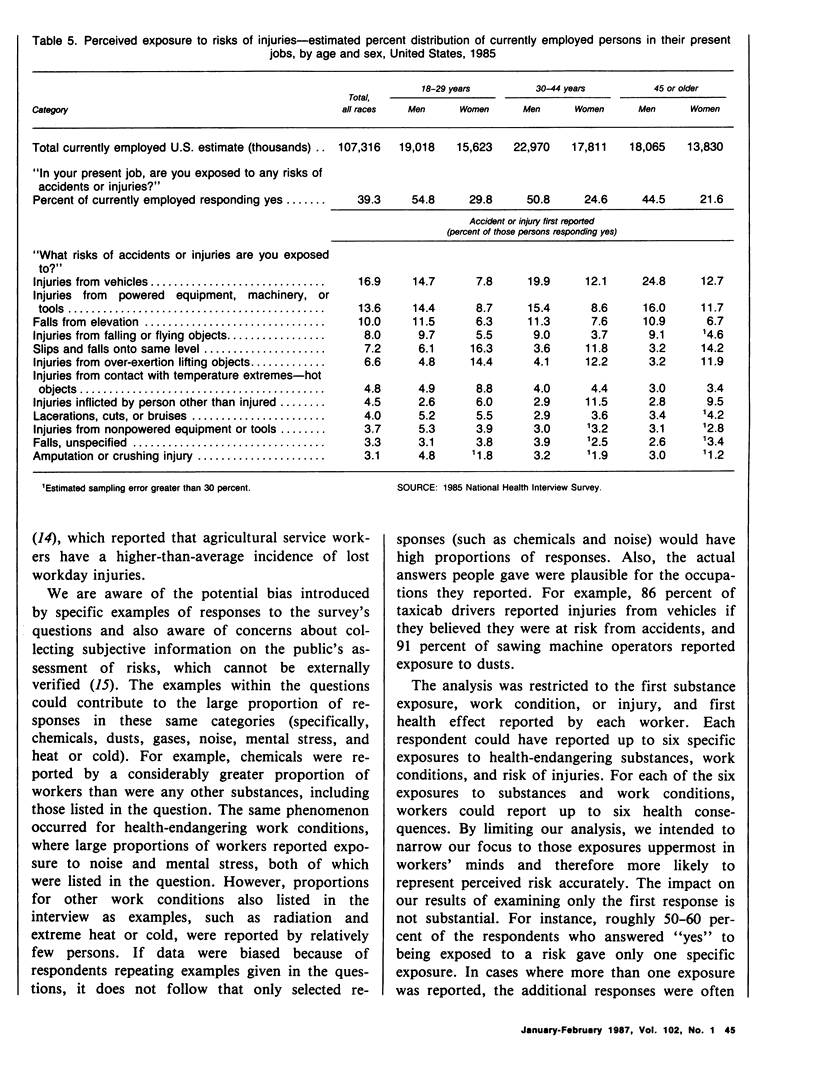
Data from the Health Promotion and Disease Prevention Questionnaire, part of the 1985 National Health Interview Survey, were used to report workers' perceptions of occupational risk in their present jobs. This information will be used to monitor progress between 1985 and 1990 toward achieving broad goals in health promotion and disease prevention. The proportions of currently employed persons who perceived exposure to health-endangering substances, work conditions, or risks of injuries were reported for age, race, sex, and occupation groups. Occupational groups were further characterized by the proportion of men and women who reported specific exposures (such as exposure to chemicals or to loud noise) and specific health consequences of exposure (such as risk of developing cancer or hearing impairment). Greater proportions of men than women reported perceived risk from exposure to health-endangering substances, work conditions, and injuries in their present job. Also, a greater proportion of workers perceived risk of injury in their present job than other occupational risk categories. The greatest proportions of perceived exposure to occupational risk were reported by farm operators and managers, police and firefighters, and by workers in forestry and fishing occupations. Among workers reporting perceived exposures, chemicals, noise, and risk of injuries from vehicles were cited by the greatest proportion of workers, as were such health consequences as lung and respiratory problems and hearing impairment. Data from this study may be used to target employment groups for health promotion or education and to develop indepth studies of specific occupational groups to reduce or prevent risk at the worksite.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Sirken M. G. Error effects of survey questionnaires on the public's assessments of health risks. Am J Public Health. 1986 Apr;76(4):367–368. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr C. Social benefit versus technological risk. Science. 1969 Sep 19;165(3899):1232–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3899.1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


