Figure 1.
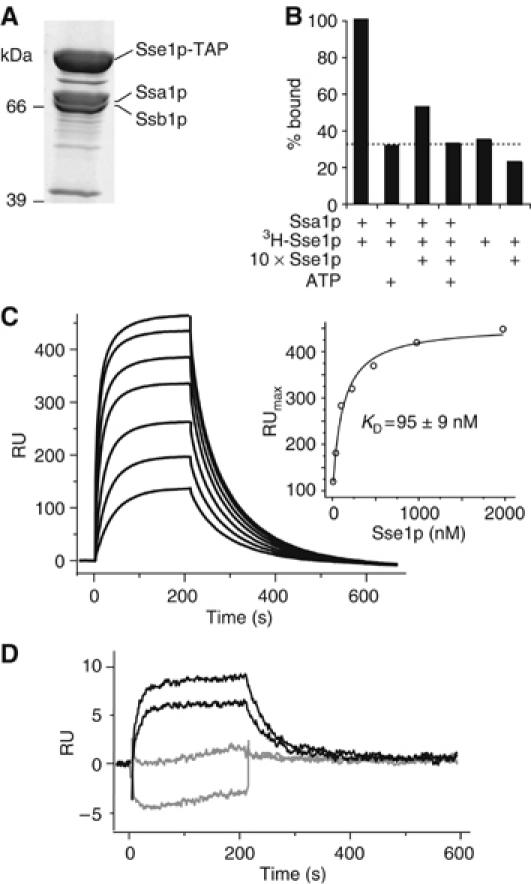
Sse1p forms stable complexes with Ssa1p and Ssb1p. (A) Purification of a TAP-tagged variant of Sse1p reveals an in vivo association with Ssa1p and Ssb1p. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation demonstrates specificity of Ssa1p–Sse1p complexes. Complexes of purified Ssa1p and 3H-Sse1p were incubated with excess unlabelled Sse1p or ATP. Levels of 3H-Sse1p that co-immunoprecpitated with Ssa1p were assessed by scintillation counting of beads. The dotted line indicates the background level of nonspecific binding of 3H-Sse1p. (C) Sensogram of interactions between Ssa1p and Sse1p. In all, 2000 RU of Ssa1p was immobilized and increasing concentrations of Sse1p injected (31.3–2000 nM in two-fold steps). Inset is maximal resonance units plotted against the respective Sse1p concentration. (D) Comparison of interactions between injected Sse1p (31.5 and 62.3 nM) and immobilized Ssa1p (150 RU) in the presence (gray) or absence (black) of 10 mM ATP.
