Figure 6.
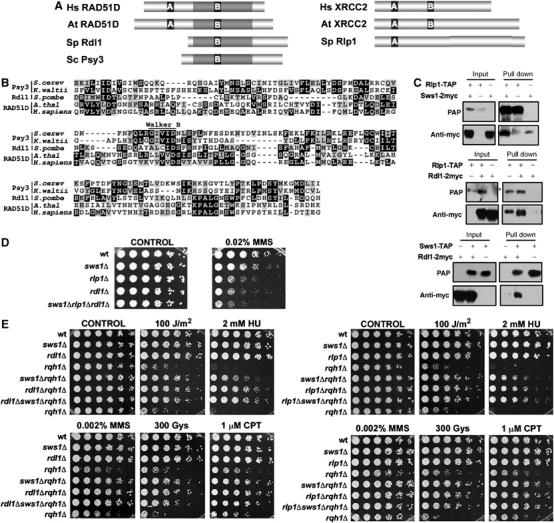
The S. pombe Rad51 paralogs, Rlp1 and Rdl1, show physical and genetic interactions with Sws1. (A) Schematic representation of the sequences of S. pombe Rdl1 and Rlp1 and their orthologs in H. sapiens (Hs), A. thaliana (At) and S. cerevisiae (Sc). A and B represent the Walker A and Walker B domains, respectively. The regions of highest similarity, centered around the Walker A and B domains are highlighted. (B) Alignment of the RAD51D family members from S. cerevisiae, K. waltii, S. pombe, A. thaliana and H. sapiens. The region of similarity between the different proteins (gray-shadowed region from the corresponding proteins in A) is shown. Conserved residues appear highlighted and the position of the Walker B motif is indicated. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of Sws1, Rdl1 and Rlp1. Cells simultaneously transformed with the appropriate Rdl1-, Rlp1- and/or Sws1-expressing vectors were used in the assay (pREP41x for 2myc tags and pREP42x for TAP tags). Cell extracts were obtained after 21 h of incubation in the absence of thiamine. *Indicates the presence of a nonspecific band. (D) Spot assay of wt (PR109), sws1Δ (VM3723), rlp1Δ (VM3741), rdl1Δ (VM3744) and sws1Δrlp1Δrdl1Δ (VM3755) strains. Four-fold serial dilutions of each strain were plated on YES plates (CONTROL) or YES supplemented with 0.02% MMS. Photographs were taken after 4 days at 32°C. (E) Serial dilutions (fourfold) of the indicated strains were plated in YES plates in the presence of different sources of DNA damage. Photographs were taken after 4 days of incubation at 32°C. Strains used in this assays: wt (PR109), sws1Δ (VM3723), rdl1Δ (VM3744), rlp1Δ (VM3741), rqh1Δ (SC3250), sws1Δ rqh1Δ (VM3722), rlp1Δ rqh1Δ (VM3740), rdl1Δ rqh1Δ (VM3745), sws1Δ rlp1Δ rqh1Δ (VM3742) and sws1Δ rdl1Δ rqh1Δ (VM3746).
