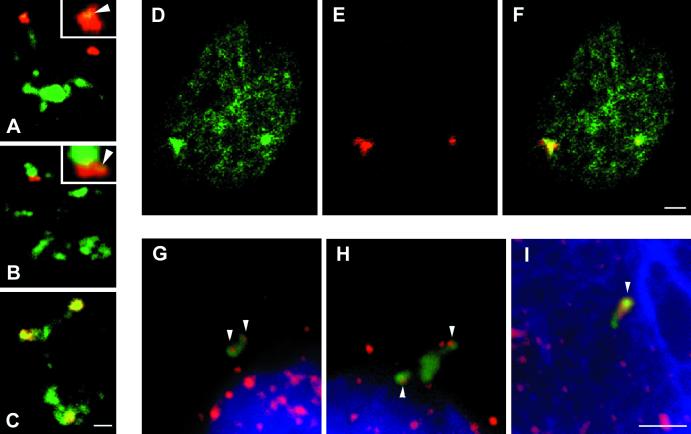
Figure 4.
Relationship between viral RNAs and SC35 domains in Raji cells and relationship among viral RNA transcript environment, visualization of nuclear domains enriched in hnRNP K/J proteins, and visualization of transcription sites in the EBV transcript environment (depicted by hnRNP K/J protein immunolabeling). The approach exploring RNA FISH (red) and immunocytochemistry has been used to establish the relationship between viral RNAs and SC35 domains in Raji cells (A–C). In most cells, one to three RNA accumulations are observed. With respect to SC35 domains, RNA signals fall within three categories. As in Namalwa cells, viral RNA is localized as either spatially distinct (A) or associated with SC35 domains (B). However, in contrast to Namalwa cells (see Figure 1), RNA accumulations inside the speckle domains are often found (C). The microclusters of splicing factors distinct from the SC35 domains at the pole of RNA accumulation are clearly visible (insets, arrowheads). By means of RNA FISH and immunocytochemistry, hnRNP K/J proteins (D, green) have been shown to be highly enriched at accumulations of viral RNA (red) in transcriptionally active Raji and Namalwa cells (E). The overlay is documented in F. This fact has been used for the localization of transcription sites at viral RNA accumulations. Visualization of transcription sites (red) in the EBV transcript environment (green) is also shown. Nuclei have been spread by osmotic shift and allowed to transcribe de novo in the presence of modified nucleotides. RNA pol II transcriptional competence has been restored by HeLa nuclear extract. Because of a highly diluted nuclear content, single sites of transcription (G–I, red) are easily distinguished. The hnRNP K/J site (K/J site), which colocalizes with the EBV transcript environment (F), is not disrupted by this method (G–I, green). One or two sites of transcription (active genes) are found in the majority of K/J sites of Namalwa spread nuclei (G and H, arrowheads). Sites of transcription colocalize with the K/J site and are of various size, usually much larger in Raji spread cells (I, arrowhead) than in Namalwa cells. Bars, 2 μm.