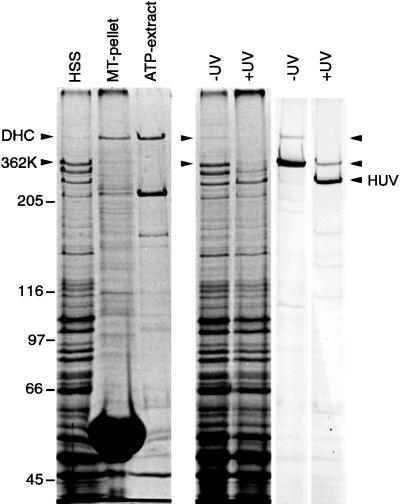
Figure 1.
Coomassie blue-stained gels showing tubulin binding and UV cleavage activity of the native DHC and 362-kDa fragment (362K) lacking the microtubule contact site. The HSS shows that substantially more 362K is expressed relative to the native DHC, but the polypeptide is not detectable in either the pellet or supernatant after incubation, sedimentation, and ATP extraction. The native DHC serves as an internal binding control and is substantially enriched in the ATP extract. The lanes marked UV show aliquots of HSS in the absence (−) and presence (+) of UV irradiation. The left panel shows a Coomassie blue-stained gel; the right panel shows a corresponding immunoblot probed with a rabbit antibody raised against a 62-kDa fragment covering the entire microtubule-binding domain (see Figure 2). Both the native DHC and the 362K fragment nearly completely disappear in the irradiated sample, evidence of efficient photocleavage for both polypeptides.