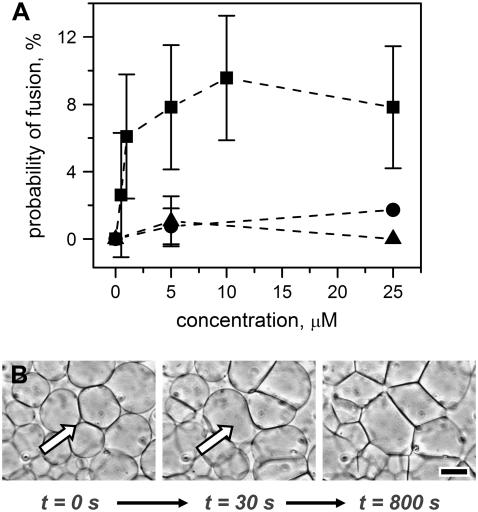
FIGURE 4.
Fusion assay for WT-B5 peptide compared with control peptides using giant liposomes composed of 90% POPC, 10% POPE. (A) We measured the average probability of fusion (defined as the number of liposomes that fused divided by the total number of liposomes in the field of view) for different concentrations of (▪) WT-B5 peptide, (•) ACTH (1–24), and (▴) the oxidized chain B of insulin. For WT-B5 peptide, the fusion probability was concentration dependent and enhanced compared to the control peptides. (B) The introduction of 5-μM WT-B5 peptide to initially spherical liposomes triggered the fusion of up to 10% of liposomes. The panels in B show a close-up of one of the fusion events at t = 30 s followed by increased interactions of membranes and two-dimensional aggregation over the course of the next 770 s. Scale bar = 40 μm.