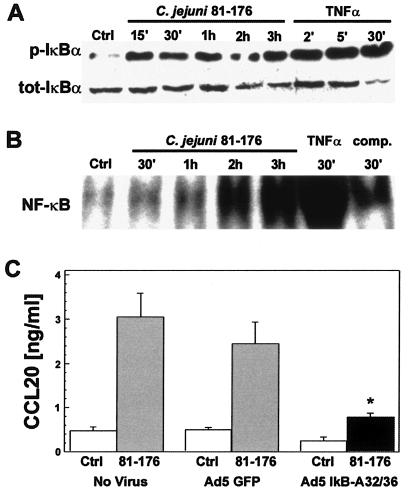
FIG. 4.
CCL20 gene expression is regulated by Campylobacter jejuni activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. A. Time course of IκBα activation in C. jejuni-infected T84 cells. Immunoblot analysis of whole-cell lysates from T84 cells infected with C. jejuni strain 81-176 (MOI of 100:1). Blots were probed with antibody to phosphorylated (p-IκBα) or total (tot-IκBα) IκBα protein. Cells were left unstimulated or were stimulated with 20 ng/ml TNF-α for 2, 5, or 30 min as negative and positive controls, respectively. Data are representative of three independent experiments. B. Nuclear extracts from C. jejuni induce the nuclear translocation of NF-κB in T84 cells. Electrophoretic mobility gel shift assays were performed using nuclear extracts from C. jejuni strain 81-176-infected (MOI of 100:1) T84 cells, obtained 30 min or 1, 2, or 3 h postinfection, and a radiolabeled probe containing an NF-κB binding site. Extracts from uninoculated cells (Ctrl) or cells stimulated with 20 ng/ml TNF-α (30 min) served as negative and positive controls, respectively. Specificity of the labeled complex was shown by incubation with unlabeled competitor probe (comp.). Data are representative of three separate experiments. C. The IκBα superrepressor inhibited CCL20 secretion. T84 cells were infected (MOI of 100:1) with recombinant adenovirus expressing either the IκBα superrepressor (Ad5IκB-A32/36) or green fluorescent protein (Ad5GFP) as indicated. Mock, uninfected cells (No Virus) were a separate internal control for Campylobacter-induced chemokine secretion. Ad5-infected cells were either inoculated with C. jejuni strain 81-176 or remained uninfected as a negative control. CCL20 secretion was assayed by ELISA as described in Materials and Methods. Values are means ± standard errors of the means for three independently completed experiments. An asterisk (*) indicates the significant difference from Campylobacter-Ad5GFP-infected cells (P < 0.05).