Table 2.
Scope of the rhodium-catalyzed allylic etherification with the copper(I) alkenyl alkoxides 2 followed by ring-closing metathesis.[a],[b]
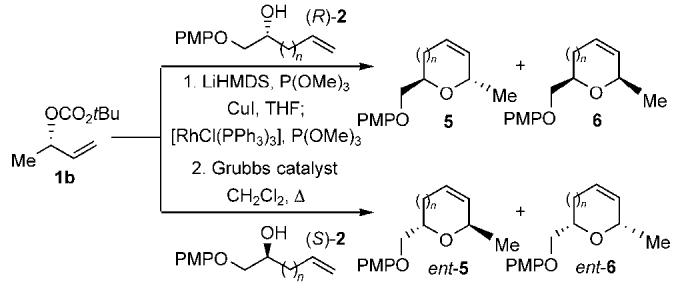
| Entry | Config. of 2 | n | d.r.[c] | Yield of addition product [%][d] | Cyclic ether | Yield [%][d] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R | 0 | 53:1 | 74 | 5a | 94 |
| 2 | S | 0 | 1:50 | 78 | ent-6a | 99 |
| 3 | R | 1 | 23:1 | 77 | 5b | 85 |
| 4 | S | 1 | 1:23 | 76 | ent-6b | 98 |
| 5 | R | 2 | 27:1 | 77 | 5c | 85 |
| 6 | S | 2 | 1:26 | 77 | ent-6c | 93 |
| 7 | R | 3 | 29:1 | 77 | 5d | 73[e] |
| 8 | S | 3 | 1:39 | 77 | ent-6d | 82[e] |
All allylic etherification reactions (0.25 mmol) were carried out with 10 mol% of the catalyst in tetrahydrofuran with 1.9 equivalents of the copper alkoxide. The regioselectivity (2°/1°) observed for the addition of the copper alkoxide was ≥99:1 in all cases. (Authentic standards were prepared independently by using copper cyanide as an additive.)
All ring-closing metathesis reactions were carried out on a 0.1-mmol scale with 5-10 mol% of the Grubbs catalyst in dichloromethane (0.1M).
Ratios of regio- and diastereoisomers were determined by capillary GLC on aliquots of the crude reaction mixture.
Yields of the isolated products.
The Grubbs N-heterocyclic carbene catalyst (0.001M) was used at reflux.
