Fig. 6.
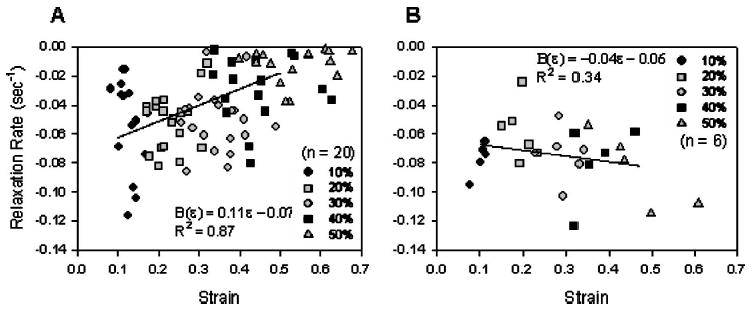
(A) The load relaxation rate parallel to the collagen fibers was dependent upon strain magnitude during ramp-hold trials. The relaxation rate was determined by normalizing relaxation curves to the peak load, then finding the slope of the log (load)-log (time) plot. The relaxation rate significantly decreased with increasing strain magnitude p <0.05 for rate at 10%, 20%, and 30% strain vs rate at 40% and 50% strain, repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey. A strain-dependent relaxation function was defined for mean rate-strain data with coefficients B ( ε) = 0.1110 ɛ − 0.0733, R 2 =0.87. (B) The load relaxation rate perpendicular to the collagen fibers was independent of strain magnitude during ramp-hold trials. A strain-dependent relaxation function was defined for mean rate-strain data with coefficients. B( ε) = −0.04 ɛ − 0.06, R 2 =0.34.
