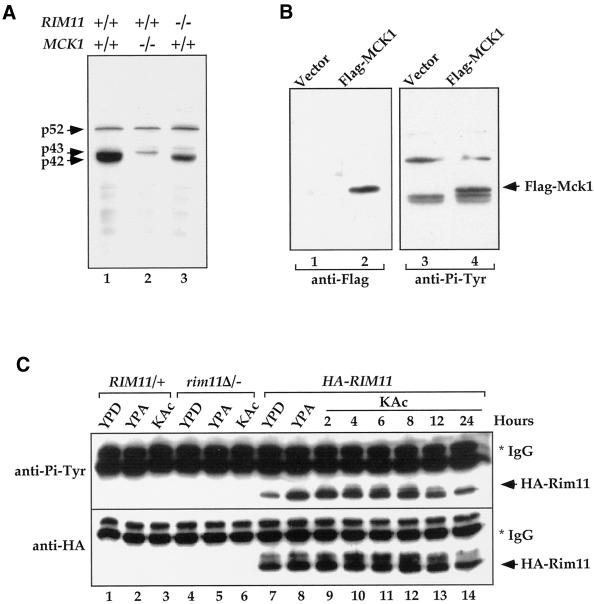
Figure 4.
Tyrosine phosphorylation of Mck1 and Rim11. (A) Deletion of MCK1 and RIM11 in ptp2Δ/− ptp3Δ/− double deletion cells eliminated Tyr phosphorylation of p42 and p43, respectively. Lysates were prepared from ptp2Δ/− ptp3Δ/− (Y164, lane 1), ptp2Δ/− ptp3Δ/− mck1Δ/− (Y165, lane 2), and ptp2Δ/− ptp3Δ/− rim11Δ/− cells (Y166, lane 3) taken 24 h after being shifted to sporulation medium. Tyr phosphorylation was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Pi-Tyr antibody. (B) Flag-tagged MCK1 is phosphorylated on Tyr in vivo. Control vector (pRS424, lanes 1 and 3) or Flag epitope-tagged Mck1 (pRS424-Flag-MCK1, lanes 2 and 4) were introduced into ptp2Δ/− ptp3Δ/− double deletion cells (Y164). Total cellular lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Flag (left, lanes 1 and 2) or anti-Pi-Tyr (right, lanes 3 and 4) antibody. Yeast cells containing epitope-tagged Mck1 showed an extra Tyr-phosphorylated band as indicated (Flag-Mck1). (C) Rim11 is phosphorylated on Tyr. Wild-type (lanes 1–3), rim11Δ/rim11Δ (KB268, lanes 4–6), or wild-type cells bearing an integrated copy of HA-RIM11 (KB600, lanes 7–14) were grown in YPD, YPA (rich acetate medium), or 1% KAc (sporulation medium). HA-Rim11 was immunoprecipitated from total cellular lysates and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Pi-Tyr (top) or anti-HA (bottom) antibody to determine Tyr phosphorylation or protein levels, respectively.