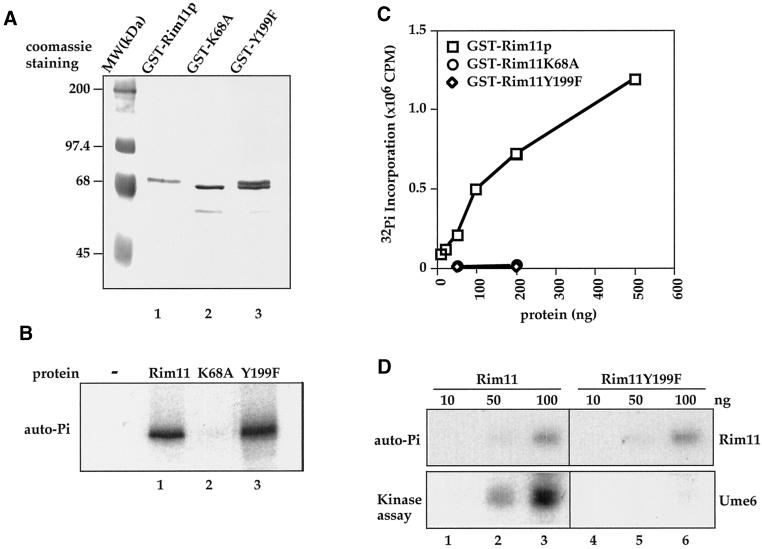
Figure 6.
Tyrosine residue 199 in Rim11 is required for the recombinant kinase to phosphorylate substrates but not for autophosphorylation. (A) Coomassie blue staining of purified GST-Rim11, K68A and Y199F protein. GST fusion proteins were expressed in E. coli and purified by glutathione-agarose affinity chromatography and Mono-Q FPLC. (B) Autophosphorylation of GST-Rim11. Equal amounts of GST-Rim11 (lane 1), K68A (lane 2), and Y199F (lane 3) were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP to allow autophosphorylation. Proteins are analyzed on SDS-PAGE and followed by autoradiography. Rim11 and Y199F showed similar autophosphorylation activity, whereas no autophosphorylation was detected on K68A. (C) Kinase activity of recombinant GST-Rim11. The indicated amounts of purified GST fusion Rim11 wild type, K68A, and Y199F were used in in vitro kinase assays with phospho-GS peptide as an artificial substrate. The radioactivity incorporated into peptide was determined by scintillation counting. Square, activity of Rim11; circle, K68A; diamond, Y199F. (D) Tyr-199 is required for Rim11 to phosphorylate Ume6, a physiological substrate of Rim11. Recombinant GST-Ume6 was used as a substrate for GST-Rim11 (lanes 1–3) or GST-Rim11Y199F (lanes 4–6) in the in vitro kinase assay. GST-Ume6 was incubated with the indicated amount of GST-Rim11 or GST-Rim11Y199F in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. The proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to autoradiography to visualize Rim11 autophosphorylation (top) or phosphorylation of Ume6 (bottom).