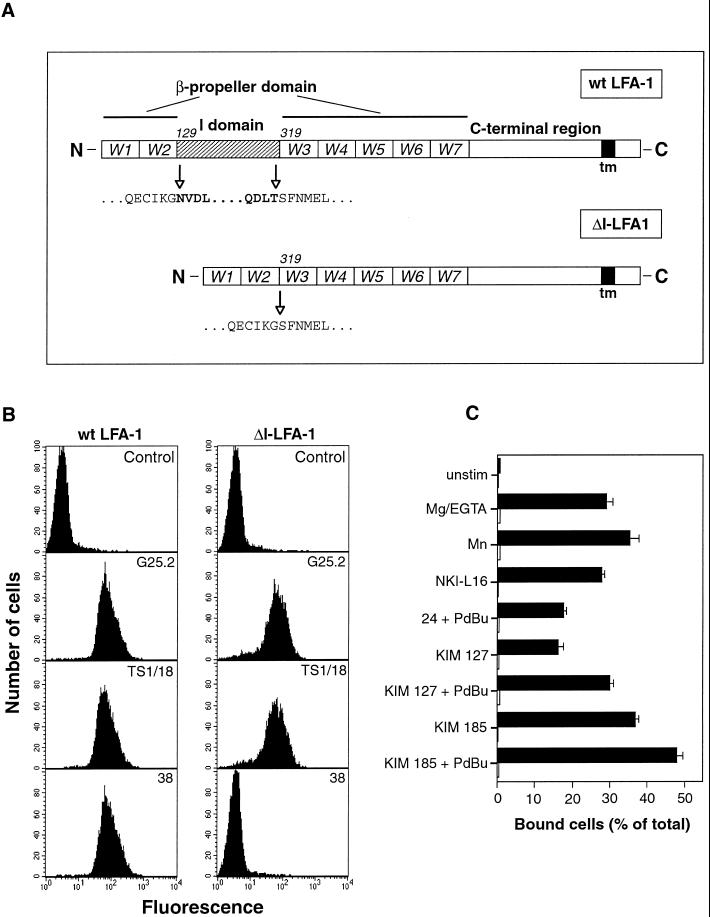
Figure 1.
Deletion of the I domain from LFA-1 and its effect on mAb epitopes and binding to ligand ICAM-1. (A) Schematic diagram of wt LFA-1 and ΔI-LFA-1 α subunits. W1–7 represent the individual β-sheets of the predicted β-propeller domain. The I domain of LFA-1 is inserted in the loop that connects β-sheets W2 and W3. Numbers (129 and 319) are positions of amino acid residues at the beginning of the I domain and of W3 of the β-propeller domain, respectively. In ΔI-LFA-1 the deletion encompasses residues N129-T318, thereby joining residue G128 to S319. tm, transmembrane domain. (B) Expression of epitopes recognized by mAbs G25.2 (anti-LFA-1 αL, epitope outside I domain), TS1/18 (anti-β2), and 38 (anti-LFA-1 αL, I domain-specific) on selected clones of J-β2.7 cells stably transfected with cDNAs encoding wt LFA-1 or ΔI-LFA-1. Cells were stained with the relevant mAbs followed by FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG and analysis by flow cytometry. As a negative control, the primary mAb was omitted. Data are representative of at least 10 determinations. (C) Adhesion of J-β2.7 cells expressing wt LFA-1 or ΔI-LFA-1 to ligand ICAM-1. Cells were allowed to bind to plastic immobilized ICAM-1 with or without stimulation for 30 min at 37°C before washing and quantification of bound cells. Stimuli were 3 mM Mg2+/1 mM EGTA, 1 mM Mn2+, and activating mAbs NKI-L16, KIM 127, KIM 185, and mAb 24. PdBu was used at 100 nM. Black bars, wt LFA-1-expressing cells; open bars, ΔI-LFA-1-expressing cells. One experiment representative of four is shown.