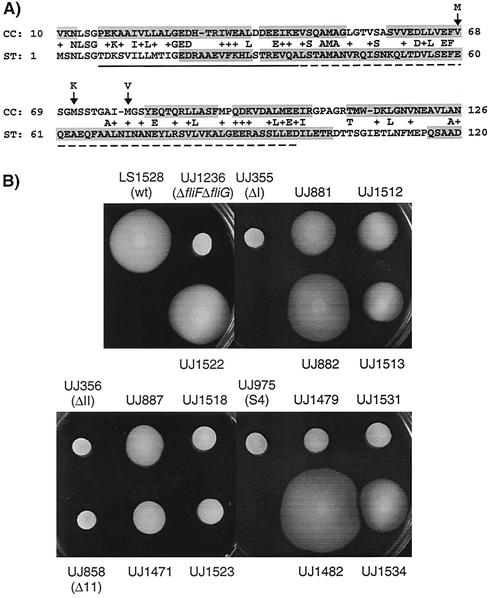
FIG. 8.
(A) Alignment of the N-terminal FliG sequences from C. crescentus (CC) and S. enterica serovar Typhimurium (ST) by using BLAST. The numbers on the sides are amino acid positions according to the sequences in the GenBank database. The solid line below the sequence indicates the amino acids essential for FliF binding in S. enterica serovar Typhimurium, and the broken line indicates amino acids that are required for proper motility (deletion mutants have reduced motility) (15). Arrows point to the amino acids that were altered in the motile suppressor strains of C. crescentus, and the letters above indicate the substituted amino acids. The shaded sequences are regions that were proposed to form α-helices by the secondary-structure prediction program PDHsec. (B) Swarming on semisolid agar of the motile suppressors with mutations in fliF or fliG, the original fliF mutants, and the Δ(fliF-fliG) tester strain complemented with the fliF-fliG loci of the suppressor strains. The strains shown are LS1528 (wild type [wt]), UJ1236 (ΔfliF-fliG), UJ1522 (UJ1236 with the fliF-fliG locus from wild-type strain LS1528), UJ355 (ΔI), UJ881 (motile suppressor of UJ355), UJ1512 (UJ1236 with the fliF-fliG locus from UJ881), UJ882 (motile suppressor of UJ355), UJ1513 (UJ1236 with the fliF-fliG locus from UJ882), UJ356 (ΔII), UJ887 (motile suppressor of UJ356), UJ1518 (UJ1236 with the fliF-fliG locus from UJ887), UJ858 (Δ11), UJ1471 (motile suppressor of UJ858), UJ1523 (UJ1236 with the fliF-fliG locus from UJ1471), UJ975 (S4), UJ1479 (motile suppressor of UJ975), UJ1531 (UJ1236 with the fliF-fliG locus from UJ1479), UJ1482 (motile suppressor of UJ975), and UJ1534 (UJ1236 with the fliF-fliG locus from UJ1482). Strains UJ883 and UJ1480 are not shown here because they contain the same mutations as strains UJ882 and UJ1482, respectively.