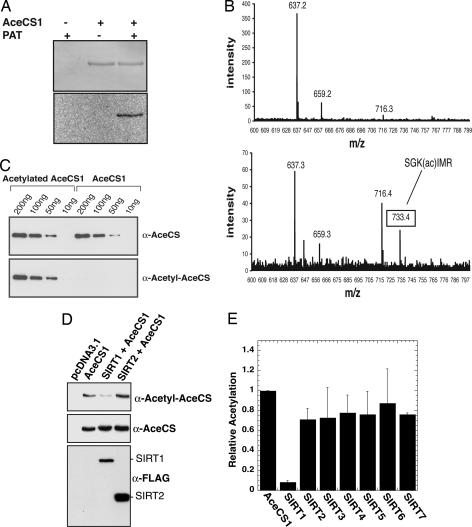
Fig. 1.
AceCS1 is acetylated in vitro and in mammalian cells. (A) AceCS1 is acetylated in vitro by PAT. Recombinant AceCS1 was incubated in the presence or absence of PAT and [1-14C]acetyl-CoA for 1h, resolved by SDS/PAGE and detected by Coomassie (Upper) and autoradiography (Lower). (B) MALDI-TOF confirms Lys-661 is acetylated on AceCS1. (Upper) Tryptic digest of AceCS1. (Lower) tryptic digest of acetylated AceCS1. As expected, the spectra are similar, with Lower showing a new peak corresponding to the acetylated peptide, SGK(ac)IMR. This peptide was further confirmed by MS/MS on the TOF–TOF instrument. (C) Acetylation state of AceCS1 can be detected with an anti-acetyl-AceCS antibody. Recombinant AceCS1 and acetyl-AceCS1 were resolved by SDS/PAGE and detected by Western blotting with anti-AceCS and anti-acetyl-AceCS antibodies, respectively. (D) Acetylation of AceCS1 is decreased upon SIRT1 coexpression. Cos-7 cells cotransfected with a construct expressing AceCS1 and the construct expressing SIRT1 or SIRT2. After 48 h, cell extracts were resolved by SDS/PAGE and detected by Western blot, using anti-acetyl-AceCS, anti-AceCS, and anti-FLAG antibodies. (E) Coexpression of AceCS1 and SIRT1–7 show increased deactylation of AceCS1 by SIRT1. The ratio of acetylated AceCS1 to total AceCS1 from cell lysates was calculated from densitometry of Western blots with anti-AceCS and anti-acetyl-AceCS1 antibodies relative to AceCS1 transfection alone.