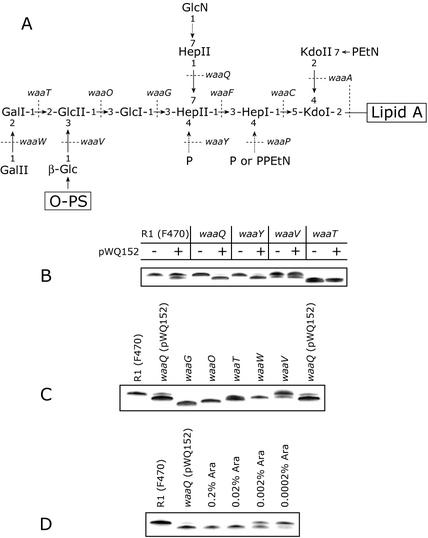
FIG. 5.
The structure of the R1 core OS and the effect of waaZ overexpression in R1 core OS mutants on LPS migration in SDS-PAGE. (A) Structure of the E. coli R1 core OS. Dashed arrows indicate nonstoichiometric substitutions. Dotted lines identify the genetic determinants involved in the indicated linkages (19). In panels A, B, and C, LPS samples were separated on a 10 to 20% Tricine gel by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining. All strains produce R-LPS, therefore only the region of the gels containing the lipid A core is shown. Expression from pWQ152 in panels B and C was induced by the addition of 0.02% l-arabinose. Panel B shows the effect of addition of multicopy WaaZ on LPS profiles in a series of R1 core OS mutants. − and +, uninduced and induced cultures, respectively. (C) Comparison of waaQ (pWQ152) LPS to core OS LPS mutant standards. The truncated LPS resulting from WaaZ overexpression comigrates with waaT LPS, a form lacking 3 sugars (note that the order synthesis also results in loss of the WaaV-added β-glucosyl residue in the waaT mutant) (19). (D) Induction of waaZ expression in waaQ (pWQ152) with various concentrations of arabinose.