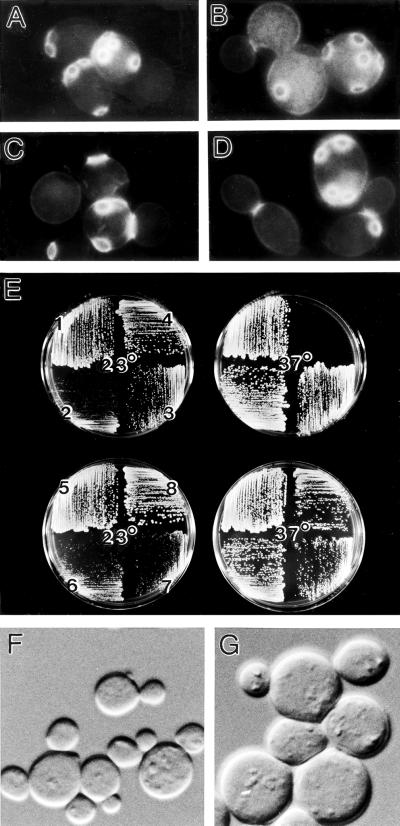
Figure 10.
Comparison of msb3 msb4, bni1, and gic1 gic2 mutant phenotypes. (A–D) Cells of diploid wild-type strain YEF473 (A), msb3Δ::HIS3/msb3Δ::HIS3 msb4Δ::TRP1/msb4Δ::TRP1 strain YEF1631 (B), bni1Δ::HIS3/bni1Δ::HIS3 strain HH799 (C), and gic1-Δ1::LEU2/ gic1-Δ1::LEU2 gic2-Δ2::TRP1/gic2-Δ2::TRP1 strain YEF1662 (D) were grown to exponential phase in YM-P liquid medium at 23°C, then fixed and stained with Calcofluor. (E) Haploid wild-type strain YEF473A (1), msb3Δ::HIS3 msb4Δ::HIS3 strain YEF1269 (2), bni1Δ::HIS3 strain YJZ426 (3), gic1-Δ1::LEU2 gic2-Δ2::TRP1 strain CCY1042–12B (4), and diploid strains YEF473 (5), YEF1631 (6), HH799 (7), and YEF1662 (8) were streaked onto YPD plates and incubated for 2 days at the indicated temperatures. (F and G) Cells of msb3 msb4 double-mutant haploid strain YEF1269 (F) and of double-mutant diploid strain YEF1631 (G) were grown to exponential phase in YM-P liquid medium at 23°C and examined by DIC microscopy. A–D, F, and G are printed at the same magnification.