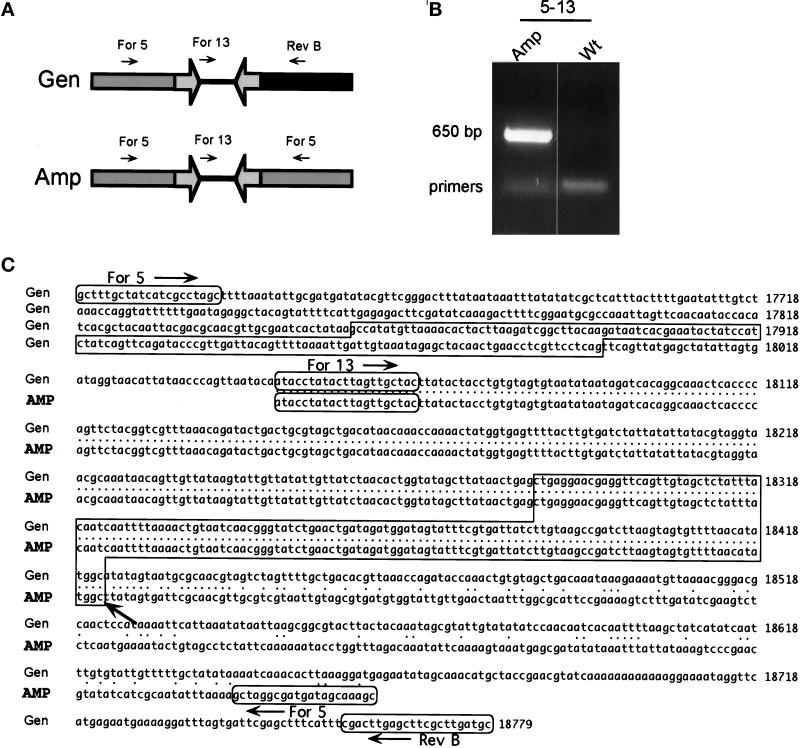
Figure 4.
Sequence of the novel joint of the 225-kb amplicon. (A) The PCR strategy used to clone the novel joint. The proposed structure of the amplicon is shown, together with the PCR primers For 5, For 13, and Rev B. Open arrows represent the inverted repeat. The primer pair For 5–For 13 together can produce a PCR product only if an inversion of one of the primers has occurred. The primer pairs For 5–Rev B and For 13–Rev B can produce products only from wild-type DNA. (B) The PCR products obtained with primers For 5 and For 13. Total DNA isolated from the wild-type (Wt) strain and from strains containing the 225-kb amplicon were used as templates for PCR. The 650-bp PCR product For 5–For 13 was observed only with template DNA from strains carrying the 225-kb amplicon. The other PCR products were observed with all templates tested, as expected (our unpublished results). (C) The sequence of the novel joint. Gen, sequence of wild-type chromosome I. Amp, sequence of the 650-bp PCR product shown in B. The inverted repeats are boxed, and the novel joint lies precisely at the end of the centromere-proximal repeat (arrow). Four independent 225-kb novel joints were sequenced, and all were identical (GenBank No. AF207956).