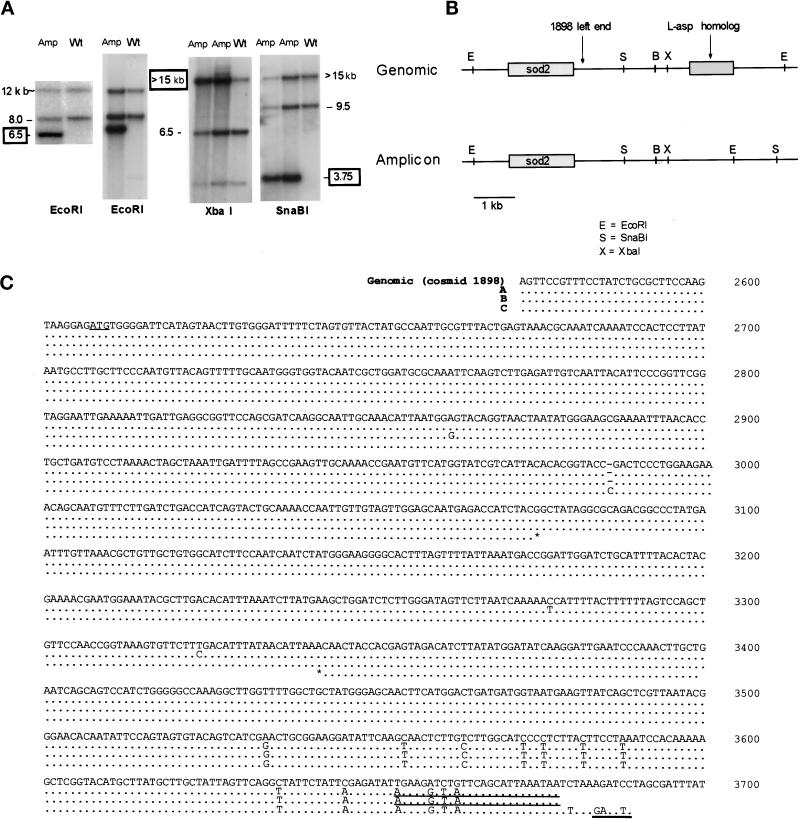
Figure 6.
A novel restriction fragment in the 180-kb amplicon. (A) Sheared genomic DNA from the wild-type (Wt) strain and from two strains carrying 180-kb amplicons (Amp) was digested with EcoRI, XbaI, or SnaBI, and the fragments were separated by gel electrophoresis. The transfers were hybridized with the 3.2-kb BamHI–EcoRI fragment of cosmid 1898. The numbers indicate sizes in kilobases. Boxed numbers indicate novel fragments detected only in strains containing the amplicon. (B) Restriction map of the novel fragment. The partial map of chromosome I is derived from our sequence and restriction data (our unpublished results). The 4.9-kb genomic fragment sequence has been submitted to GenBank (No. AF192974). (C) Sequence of the 1.1-kb novel joint PCR products from the 180-kb amplicon. The novel joint sequences have been submitted to GenBank (Nos. AF207957, AF207958, and AF207959 for A, B, and C, respectively). The region to the left (telomere-proximal) of the site of recombination is identical to the 3.2-kb BamHI–EcoRI fragment from cosmid 1898. Numbers correlate to the sequence of cosmid 1898 beginning at the telomere-proximal end. The 150 bp of sequence to the right (centromere-proximal) of the novel joints abuts the novel EcoRI site. Genomic indicates wild-type genomic DNA represented by cosmid 1898 sequence. A, B, and C represent three independent sequences. The recombination has clearly occurred in all three amplicons by bp 3534. Differences from the genomic sequence before this are believed to be Taq-induced errors. Only portions of PCR product C outside the stars were sequenced with fidelity. The underlined ATG represents the putative start site of the L-asp homologue, the longest ORF. Also underlined is the binding site of primer R-180 and the novel EcoRI site.