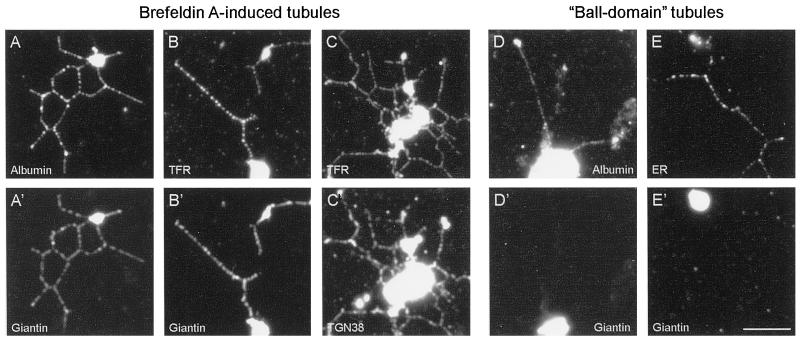
Figure 2.
Immunofluorescence analysis of BFA-induced membrane tubules and ball-domain tubules demonstrates that they contain distinct organelle markers. Networks formed in the presence of 100 μg/ml BFA (A–C and A′–C′) were processed for double-labeling immunofluorescence (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). The membrane tubules label with antibodies to the secretory marker rat albumin (A), the Golgi stack protein giantin (A′ and B′), TGN38 (C′), and transferrin receptor (B and C), demonstrating that fusion has occurred between elements of the Golgi apparatus, TGN, and early endosomes. A different class of membrane tubule, ball-domain tubules, assemble in the absence of BFA when the rat liver Golgi fraction is incubated with Xenopus egg cytosol prepared by a different method (Allan and Vale, 1994; see MATERIALS AND METHODS). Unlike BFA tubules, the ball-domain tubules do not contain giantin (D′ and E′) but do label with antibodies against rat albumin (D) and the mAb 1D3 (E), which recognizes KEDL-containing proteins in the ER. Bar, 5 μm (applies to all panels).