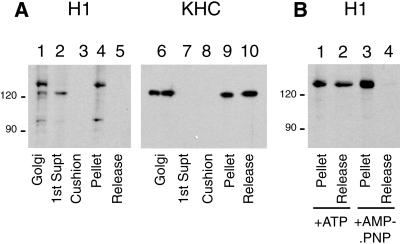
Figure 6.
Identification of candidate motor proteins for BFA-induced membrane tubule formation. (A) Biochemical analysis of motor and microtubule binding. Rat liver Golgi membranes were solubilized and incubated with microtubules under conditions that promote motor binding. Microtubules were recovered by centrifugation, and the proteins present in the remaining supernatant fraction (lane 2 and 7) and the cushion fraction (lane 3 and 8) were recovered by precipitation. The microtubule pellet was resuspended in buffer containing 5 mM ATP and 100 mM KCl and centrifuged to give a microtubule pellet (lanes 4 and 9) and an ATP release supernatant (lanes 5 and 10). Untreated Golgi fraction was loaded in lanes 1 and 6. After SDS-PAGE, protein samples were immunoblotted with either the H1 monoclonal antibody (lanes 1–5) or the polyclonal anti-uKHC antibody (lanes 6–10). (B) Microtubule pellets with rigor-bound motors were incubated with buffer containing 0.5 M NaCl plus either 5 mM ATP (lanes 1 and 2) or 5 mM AMP.PNP (lanes 3 and 4). Microtubule pellets (lanes 1 and 3) and release fractions (lanes 2 and 4) were resolved by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with the H1 antibody.