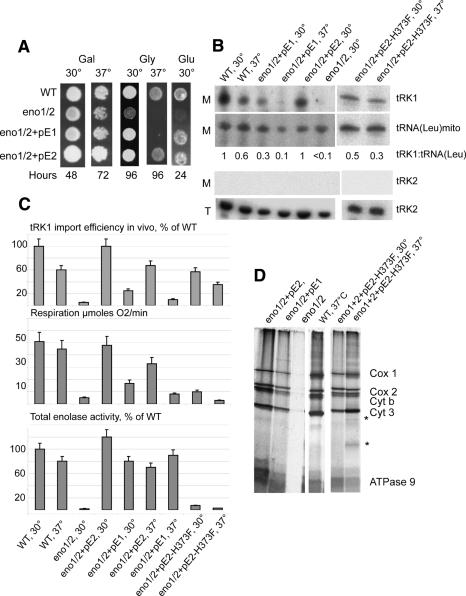
Figure 4.
Effect of ENO1/2 genes inactivation on tRK1 import and mitochondrial functions. (A) The effect of ENO1 and ENO2 genes deletion on yeast cells growth on nonfermentable carbon source (Glycerol [Gly] YPEG medium), YPGal medium (Gal), or YPD (Glu). Culture growing temperature is indicated above the panel, the duration of growing, at the bottom (hours). (WT) Wild-type strain W303; (+pE1 and +pE2) strains expressing Eno1p or Eno2p from centromeric plasmids pE1 or pE2. (B) The effect of ENO2 gene deletion or mutation on tRK1 import in vivo. Northern hybridization detection of tRK1 and control tRNAs [mitochondrial tRNA(Leu) and cytoplasmic nonimported tRNA(Lys), tRK2] are presented. On the left, M indicates RNA isolated from purified mitochondria, and T indicates total RNA. Strains and temperature of cultivation are indicated on top. (eno1/2) eno1 eno2 deletant strain; (pE2-H373F) plasmid expressing Eno2p with substitution H373F. Equal amounts of RNAs were analyzed for each strain. The ratio between the signals for tRK1 and mt tRNA (Leu) used as a criterion of import efficiency is presented in the middle. (C) Quantification of tRK1 import efficiency, respiration, and enolase enzymatic activity in the crude cell lysates of different strains (listed on the left side of the panel). (D) Effect of ENO2 gene deletion or mutation on mitochondrial translation. The autoradiograph of the PAGE-separated [35S]-labeled mitochondrially synthesized polypeptides is presented. Strains and the temperature of incubation during the translation reaction are indicated above. Polypeptides were identified by comparison with standard mitochondrial translation pattern (McKee et al. 1984). (Cox 1, 2, and 3) Subunits 1–3 of cytochrome c oxidase; (Cyt b) cytochrome c; (ATPase 9) subunit 9 of ATP synthase. Additional bands appearing at 37°C with the H373F Eno2p version are indicated with the asterisks.