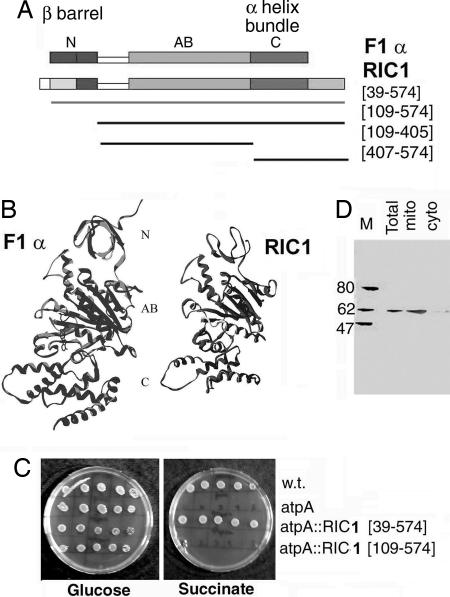
Fig. 1.
Structural and functional homology of RIC1 with ATP synthase subunit α. (A) RIC1 and AtpA conserved domain (COG0056) of F1 ATP synthase subunit α, showing N-terminal (N), ATP binding (AB), and C-terminal (C) domains. (B) Homology model of RIC1 secondary structure backbone compared to that of bovine F1 ATPase α subunit. (C) Complementation of E. coli AtpA mutation by Leishmania RIC1. Serial dilutions (from 105 to 10 cells, left to right) of strain AN120 (AtpA), strain AN180 (the isogenic wild-type) or AN120 transfected with RIC1[39–574] or RIC1[109–574] were spotted on minimal media containing either glucose or succinate as carbon source. (D) Immunoblot of protein (100 μg) of total, mitochondrial (mito), or cytosolic (cyto) fractions of L. tropica promastigotes using anti-RIC1 serum as probe.