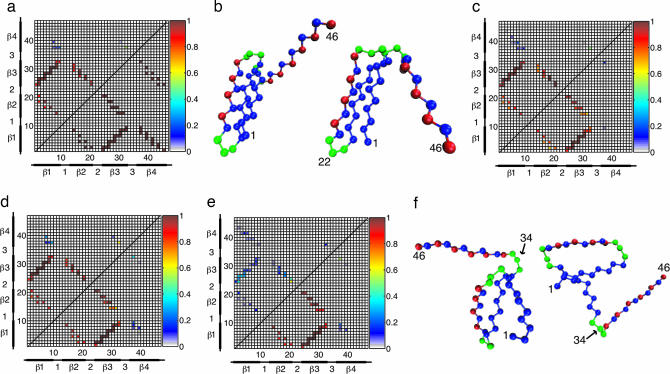
Fig. 3.
TS native contact maps and representative structures. (a) Native contact map for the bulk TS (upper quadrant). The native contact map for the native state is shown in the lower quadrant for comparison. (b) Representative TS structures for the bulk (Left) and tether point 22 (Right). The structures are very similar, with well formed hydrophobic cores. (c and d) TS native contact maps for tether points 1 (c, upper quadrant), 11 (c, lower quadrant), 22 (d, upper quadrant), and 46 (d, lower quadrant). The native contact maps for these tether points are qualitatively similar to each other and the bulk TS. In this respect, the structures shown in b are representative TS structures for all tether points except 34. (e) TS native contact map for tether point 34 (upper quadrant) with the bulk TS map (lower quadrant) shown for comparison. (f) Two representative TS structures for this tether point. In contrast to the other tether points and the bulk, tether point 34 has a highly unstructured TS. Moreover, whereas the TS structures for the bulk and other tether points are relatively homogeneous, the TS for tether point 34 has a significant amount of structural diversity, as evidenced in part by the example structures shown in f.