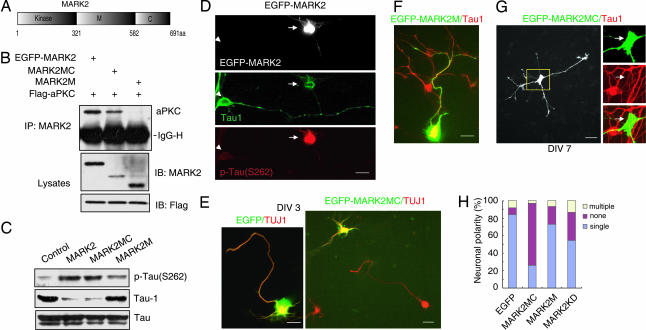
Fig. 3.
The role of MARK2 and its mutants in neuronal polarity. (A) Schematic diagrams of MARK2 structure. (B) HEK-293 cells were transfected with Flag-PKCζ and EGFP-tagged MARK2 constructs. The immunoprecipitates with anti-MARK2 antibody were subjected to immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. IgG-H, IgG heavy chain. (C) Primary neurons were transfected with MARK2 constructs or control plasmid and cultured for 48 h. The levels of different tau isoforms were accessed by immunoblotting. (D) Neurons transfected with EGFP-MARK2 were stained at DIV3 with antibodies against different tau isoforms, Tau1, and p-tau (S262). Note that the EGFP-MARK2-positive cell (arrow) stained strongly for p-tau (S262) but weakly for Tau1, in comparison with the nontransfected cell (arrowhead). (E) Neurons transfected with EGFP-MARK2MC or EGFP were stained with anti-TUJ1 antibody at DIV3. Note that EGFP-MARK2MC-expressing cells were unpolarized, whereas the neighboring untransfected cells were polarized. (F) Neurons transfected with EGFP-MARK2M were stained with Tau1 antibody at DIV3. (G) Neurons transfected with EGFP-MARK2MC were stained with Tau1 antibody at DIV7. Note that MARK2MC-expressing cells (arrows) stained low for Tau1 signal in comparison with the neighboring nontransfected cell. (H) Quantitative analysis of neuronal polarity. None, neurons with short neurites in similar length; single, neurons with one Tau1-positive process >100 μm and at least twice as long as the second longest process; multiple, neurons with two or more Tau1-positive processes >100 μm and twice as long as other neurites. The data were obtained from three independent experiments. At least 90 cells for each construct were analyzed per experiment.