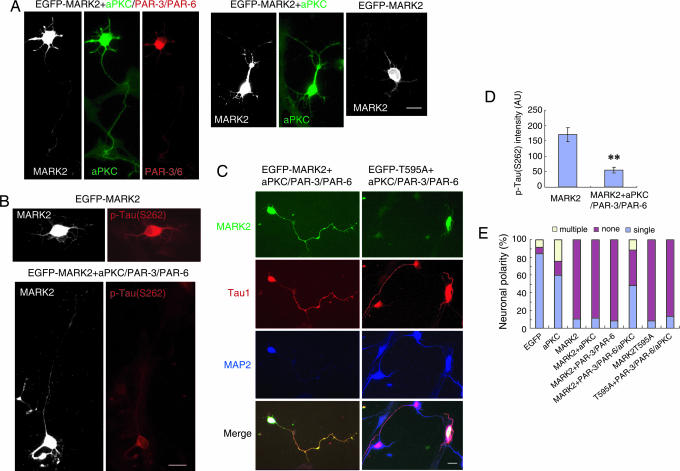
Fig. 4.
The PAR-3/PAR-6/aPKC complex counteracts the polarity defect caused by ectopic MARK2 expression. (A) Hippocampal neurons were transfected with EGFP-MARK2, together with Flag-aPKC, or hemagglutinin (HA)-PAR-3 plus PAR-6, or Flag-aPKC plus PAR-3 and PAR-6 with the ratio of 1:3:3:3 (MARK2/PAR-3/PAR-6/aPKC). Transfected cells at DIV3 were stained with rabbit polyclonal antibody against aPKC and mouse monoclonal antibody against HA to monitor levels of exogenously expressed aPKC and PAR-3/6. Immunoreactivity was visualized by Alexa Fluor 350-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody and rhodamine-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody, respectively. Shown are the examples of hippocampal neurons transfected with various plasmid combinations. (B) Neurons transfected with EGFP-MARK2, and with or without aPKC plus PAR-3 and PAR-6, were stained with antibody against p-tau (S262) at DIV3. (C) Neurons were transfected with EGFP-MARK2 or the T595A mutant, together with aPKC plus PAR-3 and PAR-6 (1:3:3:3), and stained with antibodies against Tau1 and MAP2 at DIV3. (D) Quantitative analysis of the immunofluorescence intensity of p-tau (S262). The intensity of p-tau (S262) in GFP-MARK2-positive cells, with or without PAR-3/PAR-6/aPKC, was plotted. AU, arbitrary unit. Data are shown as means ± SEM (n = 13; ∗∗, P < 0.01). (E) Quantitative analysis of polarity phenotype. The data were obtained from three independent experiments. At least 90 cells for each transfection were analyzed per experiment.