Figure 4.
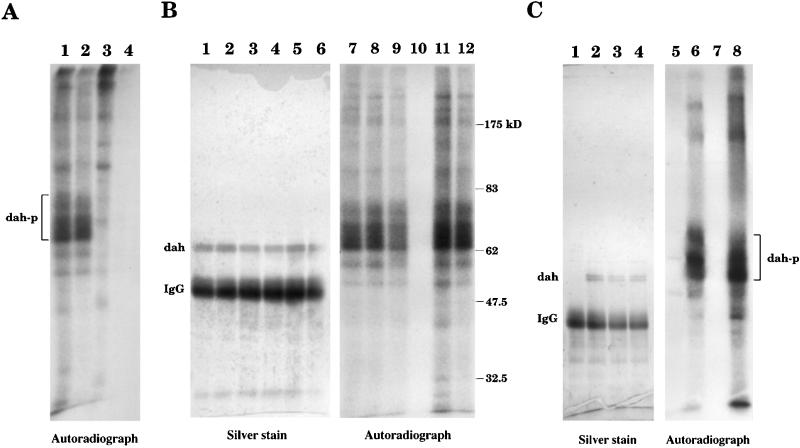
A kinase activity is found in DAH immune complex. (A) Immunoprecipitation with the wild-type 0- to 4-h embryonic extract was carried out by the DAH antibody (lanes 1 and 2) or the preimmune serum (lanes 3 and 4). The immune complex was washed and incubated with [γ-32P]ATP for in vitro kinase assay. Washing with 150 mM NaCl (in buffer N) was used for lanes 1 and 3, and 1 M NaCl was applied for lanes 2 and 4. The samples were loaded onto a gel and subjected to autoradiography. A series of phosphorylated bands were specifically detected in the DAH immunoprecipitates. (B) The DAH immune complex was washed with 150 mM NaCl (lanes 1 and 7), 1 M NaCl (lanes 2 and 8), 4.5 M NaCl (lanes 3 and 9), 1 M KI (lanes 4 and 10), 10 mM EGTA (lanes 5 and 11), and 10 mM EDTA (lanes 6 and 12), all in buffer N, before the kinase reaction. The gel was stained by silver stain (lanes 1–6) and then exposed to a film (lanes 7–12). The kinase activity, but not the DAH protein itself, can be washed off by 1 M KI (lanes 4 and 10). (C) Immunoprecipitation was carried out with the mutant extract (lanes 1 and 5) or the wild-type extract (lanes 2 and 6) before the kinase assay. DAH protein was not detected in the mutant. When the DAH immune complex from the wild-type extract was washed with 1 M KI (lanes 3, 4, 7, and 8), the kinase activity was recovered after the incubation with the mutant extract (lane 8). No activity was observed when the DAH complex was incubated with the homogenization buffer alone (lane 7). dah-p, phosphorylated DAH; IgG, immunoglobulin G.