Figure 3.
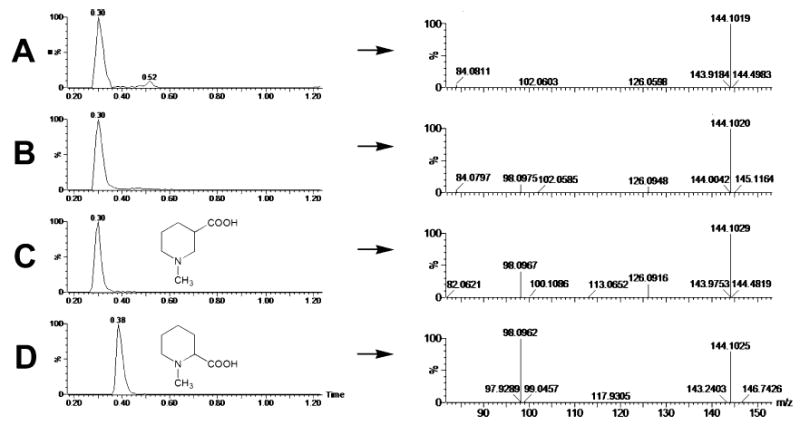
Identification of N-methylnipecotic acid as a metabolite of arecoline by LC–MS/MS. (A) Single-ion chromatogram (m/z = 144.1) of urine from an untreated mouse, showing a single major peak eluting at 0.30 min in 20 mM ammonium formate (pH 6.4). The positive-ion MS/MS spectrum shows a [M +H]+ion at 144.102 m/z and a fragment ion at 84.081 m/z. (B) Single-ion chromatogram (m/z = 144.1) of urine from a mouse treated with arecoline (20 mg/kg p.o.), showing a single peak eluting at 0.30 min in 20 mM ammonium formate (pH 6.4). The positive-ion MS/MS spectrum shows a protonated ion at 144.102 m/z and fragment ions at 98.098 and 126.095 m/z. (C) Single-ion chromatogram (m/z = 144.1) of a 10 μM aqueous solution of N-methylnipecotic acid, showing its chemical structure and a single peak eluting at 0.30 min in 20 mM ammonium formate (pH 6.4). The positive-ion MS/MS spectrum shows a protonated ion at 144.103 m/z and fragment ions at 98.097 and 126.092 m/z. (D) Single-ion chromatogram (m/z = 144.1) of a 10 μM aqueous solution of N-methylpipecolic acid, showing its chemical structure and a single peak eluting at 0.38 min in 20 mM ammonium formate (pH 6.4). The positive-ion MS/MS spectrum shows a protonated ion at 144.103 m/z and a large fragment ion at 98.096 m/z.
