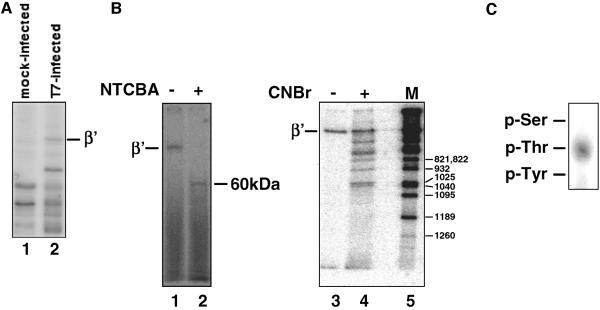
FIG. 1.
Localization of the β′ phosphorylation site by use of chemical proteases. (A) E. coli MG1655 cells were infected with bacteriophage T7 in the presence of radioactive orthophosphate as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were collected and lysed, proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and phosphoproteins were revealed by autoradiography. Lane 1 shows phosphoproteins in control, mock-infected cells. The position of the E. coli RNAP β′ subunit is indicated. (B) 32P-labeled RNAP was purified from T7-infected cells prepared as described for panel A and subjected to complete proteolysis with Cys-specific NTCBA (left panel) or limited proteolysis with Met-specific CNBr (right panel). Met residues are labeled at right (right panel). The products were resolved by SDS-PAGE and revealed by autoradiography. (C) 32P-labeled RNAP β′ from T7-infected cells was subjected to complete acid hydrolysis, and phosphoamino acids were revealed, after thin-layer chromatography, by autoradiography. Positions of phosphoamino acid markers are indicated.