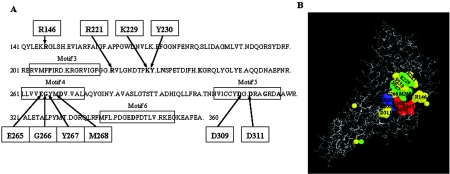
FIG. 1.
Conserved amino acids of the catalytic center of E. coli primase. (A) Conserved residues in bacterial primase core domains are in bold type. The data were taken from Keck et al. (10). Arg146, Arg221, Lys229, Tyr230, Gly266, Tyr267, Met268, Asp309, and Asp311, which were changed to Ala by oligonucleotide mutagenesis, are indicated with arrows. Glu265 was changed to Gln, not Ala. (B) Crystal structure of the catalytic core fragment of E. coli primase. The locations of conserved amino acids studied are shown. Asp269, Asp345, and Asp347 amino acids bind Mg2+ ions and create the active site of the enzyme (7). They are shown in red. Glu265 and Asp309 amino acids are shown in blue. Lys229, Tyr267, and Met268 amino acids are shown in green. Arg146, Arg221, Tyr230, Gly266, and Asp311 amino acids are shown in yellow.