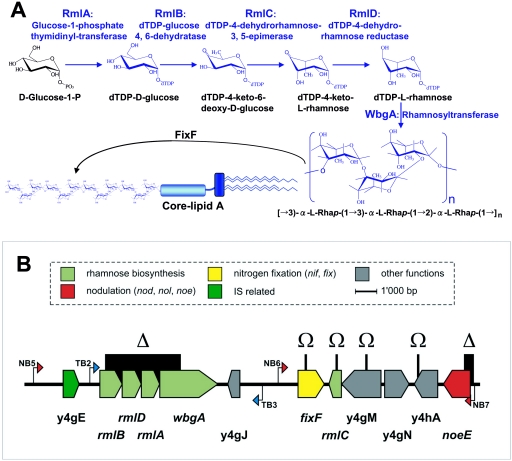
FIG. 1.
A. Proposed synthetic pathway of rhamnose and its possible adjunction to the LPS core by enzymes encoded within the 87°-110° locus. The putative roles of the RmlA to -D enzymes in the synthesis of dTDP-l-rhamnose from d-glucose-1-phosphate are shown. A predicted glycosyl transferase, WbgA, could be responsible for the polymerization of the newly synthesized rhamnose residues. FixF is thought to function in the export or attachment of the rhamnose-rich O antigen across the bacterial membrane or onto lipid A core molecules. B. Genetic map of the 87°-110° locus of Rhizobium sp. strain NGR234. Genes are drawn as arrows matching the sense of transcription and are colored according to their proposed function. nod boxes and tts boxes are represented by red and blue arrows, respectively. The positions of the various mutations are shown above the genes as either omega cassette insertions (Ω) or deletions followed by omega cassette insertions (Δ).