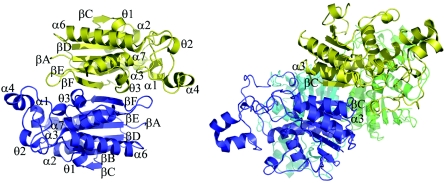
FIG. 2.
Oligomerization. (Left) The Rv3214 dimer, viewed down the approximate twofold axis relating the two monomers, shown in blue and gold. The C-terminal β-strands (βF) of the two monomers run in an antiparallel fashion, making several hydrogen bonds, and the βE-βF loop of each monomer extends over the active site of the other monomer. (Right) The tetrameric S. cerevisiae dPGM (5, 36, 39), shown for comparison. In this case, the βC strands and the small subdomain are used in oligomerization.