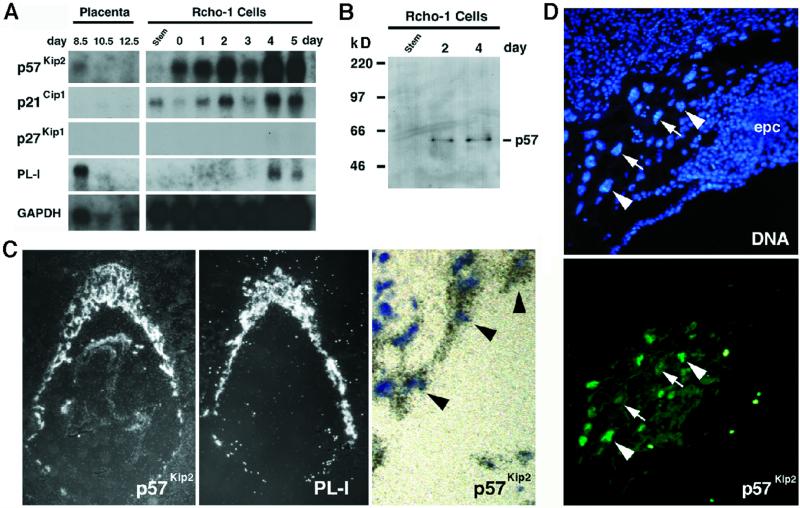
Figure 1.
Expression of the Cdk-inhibitor p57Kip2 in trophoblast giant cells. (A) Northern blot analysis of Cip1, Kip1, and Kip2 expression. RNA from placentas and proliferating stem and differentiating Rcho-1 giant cells was isolated at the indicated times during development, transferred to filters, and hybridized with radiolabeled cDNA probes. Placental lactogen-I (PL-I) is exclusively expressed in trophoblast giant cells. Filters were rehybridized with a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase probe to control for RNA loading. (B) Protein immunoblot of p57Kip2. Extracts were prepared from Rcho-1 stem as well as day 2 and 4 giant cells and subjected to immunoblot analysis. A single band migrating at 57 kDa was recognized in trophoblast giant cell extracts. (C) Localization of Kip2 mRNA by in situ hybridization of E8.5 mouse conceptuses. Silver grains, visualized under dark-field microscopy, localized to trophoblast giant cells, as well as specific regions of the embryo. An adjacent section was hybridized with an probe for PL-I, a marker of trophoblast giant cells. Under high-power light microscopy, (far right panel), note a single layer of trophoblast giant cells (black arrowheads), distinguishable by their large nuclei, that all contain silver grains. (D) p57Kip2 protein localization to trophoblast giant cells. Immunolocalization of p57Kip2 protein in trophoblast cells. Unlike the Kip2 mRNA, which was present in all trophoblast giant cells, the protein was detectable in only a subset of giant cell nuclei (arrowheads indicate positive cells, whereas arrows indicate negative cells). In addition, p57Kip2 protein was undetectable in trophoblast cells of the ectoplacental cone (epc).