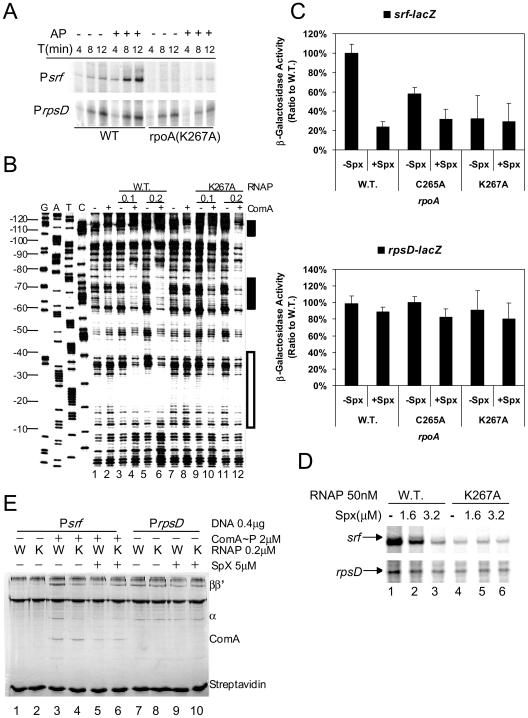
FIG. 6.
Effect of rpoA(K267A) mutation on ComA-dependent srf transcription and Spx-dependent repression. (A) Time course in vitro transcription experiment showing the accumulation of srf transcript in reaction mixtures containing untreated (−) or acetyl phosphate (1.6 mM)-treated (+) ComA, and either wild-type RNAP (WT) or rpoA(K267A) RNAP (50 nM). (B) Denaturing gel analysis of DNase I footprint reactions containing Psrf DNA with (+) and without (−) ComA∼P in the presence of wild-type RNAP (WT) or RpoA(K267A) RNAP. RNAP was used at 0.1 μM and 0.2 μM as indicated. (C) Effect of SpxLDD production on levels of β-galactosidase activity in srf-lacZ (ORB6129, ORB6131, and ORB6132) and rpsD-lacZ (ORB6137, ORB6139 and ORB6140) cells bearing the wild-type rpoA allele or the rpoA(C265A) or rpoA(K267A) mutant allele. srf-lacZ fusion-bearing cells were collected from cultures at the end of exponential growth, while rpsD-lacZ cells were collected from mid-log-phase cultures. (D) Effect of Spx (1.6 μM) on transcription of srf in reaction mixtures containing ComA (1.6 μM), acetyl phosphate (1.6 mM), and either wild-type (WT) or rpoA(K267A) RNAP (50 nM). Control transcripts from reactions containing rpsD promoter DNA are shown at the bottom. (E) Effect of rpoA mutations on ComA-dependent RNAP binding to the srf and rpsD promoter and on Spx-dependent RNAP release from promoter DNA. SPPR reaction mixtures contained ComA (+) and either wild-type (W) or rpoA(K267A) (K) RNAP in the presence (+) or absence of Spx.