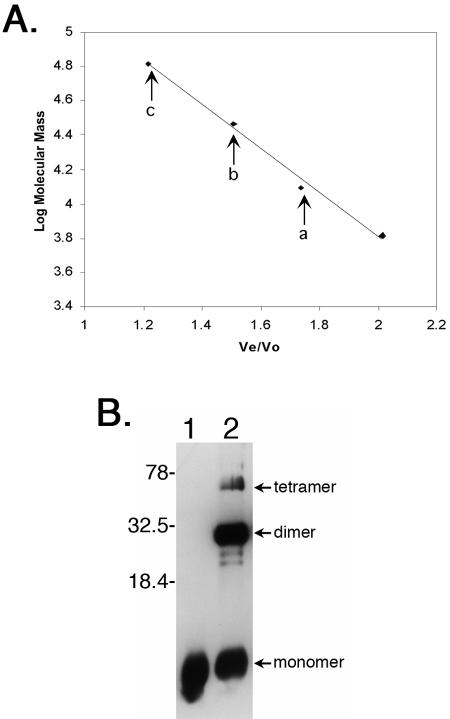
FIG. 5.
EbfC forms dimers and higher-ordered multimers in solution. (A) Size fractionation analysis of recombinant EbfC, with arrows denoting Ve/V0 values of three 280-nm-absorbing peaks corresponding to monomer (a), dimer (b), and tetramer (c) forms of the protein, having apparent molecular masses of 13,800, 26,900, and 64,100 Da, respectively. Diamonds indicate elution positions of molecular mass standards, left to right: bovine serum albumin (66,000 Da), bovine carbonic anhydrase (29,000 Da), horse heart cytochrome c (12,400 Da), and bovine lung aprotinin (6,500 Da). (B) Cross-linking of purified recombinant EbfC in solution. Lane 1, no formaldehyde cross-linking agent added; lane 2, protein incubated with formaldehyde. Protein bands with molecular masses corresponding to monomeric, dimeric, and tetrameric EbfC are indicated. Note that the recombinant protein is larger than wild-type EbfC due to the inclusion of the N-linked polyhistidine tag and linker residues (approximately 14 kDa versus 11 kDa for native EbfC). Numbers on the right indicate positions of molecular mass standards.