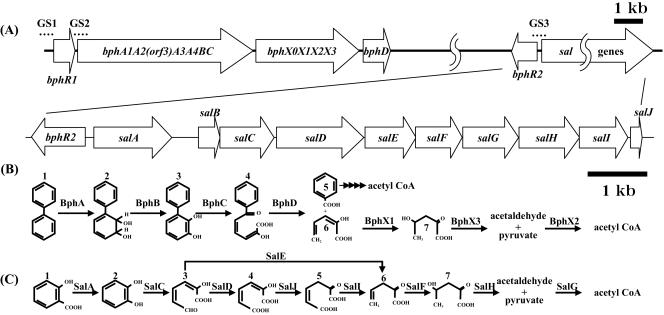
FIG. 1.
Organization of bph and sal gene clusters (A) and catabolic pathways of biphenyl (B) and salicylate (C) in P. pseudoalcaligenes KF707. (A) GS1 (161 bp), GS2 (123 bp), and GS3 (166 bp) used in the gel shift assays are indicated by dotted lines. (B) Compounds involved in biphenyl catabolism are indicated as follows: 1, biphenyl; 2, 2,3-dihydroxy-4-phenylhexa-4,6-diene; 3, 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl; 4, HOPD; 5, benzoic acid; 6, 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoic acid; and 7, 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate. The enzymes and proteins involved are biphenyl dioxygenase (BphA), dihydrodiol dehydrogenase (BphB), 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl dioxygenase (BphC), 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate hydrolase (BphD), 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoate hydratase (BphX1), 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate aldolase (BphX3), and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (BphX2). (C) Compounds involved in salicylate catabolism are indicated as follows: 1, salicylate; 2, catechol; 3, HMSA; 4, 2-hydroxyhexa-2,4-diene-1,6-dioate; 5, 2-oxohexa-3-ene-1,6-dioate; 6, 2-oxopent-4-enoate; and 7, 4-hydroxy-2-oxovalerate. The enzymes and proteins involved are salicylate hydroxylase (SalA), catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (SalC), hydroxymuconic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SalD), 4-oxalocrotonate isomerase (SalJ), 4-oxalocrotonate decarboxylase (SalI), 2-oxopent-4-enoate hydratase (SalF), 2-oxo-4-hydroxypentanoate aldolase (SalH), and hydroxymuconic semialdehyde hydrolase (SalE). acetyl CoA, acetyl coenzyme A.