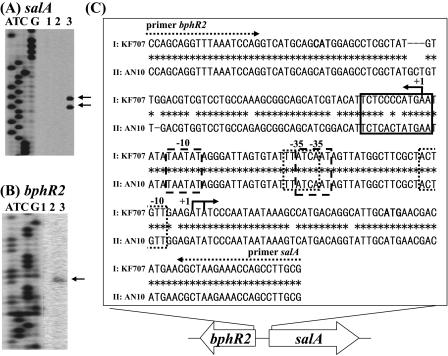
FIG. 2.
Transcriptional initiation sites of salA (A) and bphR2 (B) and possible functional regions (C). (A and B) The end-labeled primers were complementary to regions located 14 bp or 6 bp downstream of the salA and bphR2 start codons, respectively. Lanes A, T, C, and G show the results of the dideoxy sequencing reaction carried out with the M13 forward primer. Lane 1, primer extension reaction with RNA prepared from KF707 cells grown with succinate; lane 2, primer extension reaction for cells grown with biphenyl plus succinate; lane 3, primer extension reaction for cells grown with salicylate plus succinate. The arrows indicate the transcriptional initiation sites. (C) Sequences I and II indicate the regions between the bphR2 and salA genes in KF707 and between the nahR and nahG genes in P. stutzeri AN10 (GenBank accession no. AF039534), respectively. Possible −10 and −35 promoter regions for bphR2 and sal genes are indicated by dotted boxes. The possible binding stretch (T-N11-A) of NahR is indicated by a box. The dotted arrows indicate the primers. The solid arrows indicate transcriptional initiation sites of bphR2 and salA. The start codons of bphR2 and salA are indicated by boldface type.