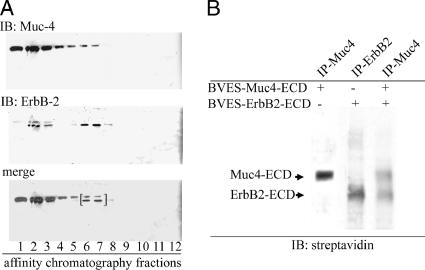
Figure 1.
Isolation of soluble Muc4–ErbB2 complex from insect cells and confirmation of complex formation and determination of its stoichiometry by biotinylation. The extracellular domains of Muc4 (≈120 kDa) and histidine-tagged ErbB2 (≈90 kDa) were coexpressed in High-5 insect cells as described in Materials and Methods. Insect cell lysates were fractionated by affinity chromatography to isolate His-tagged proteins. (A) Immunoblot analysis to locate the fractions containing the Muc4–ErbB2HIS complex using a mAb 4f12 against Muc4 (Rossi et al., 1996) and anti-ErbB2 Neomarkers 10. Fractions 6 and 7 containing complex were combined, immunoprecipitated with anti-Muc4, and biotinylated with EZ-Link Sulfo-NHS-Biotin. Bracket indicates fractions used for anti-Muc4 immunoprecipitation and biotinylation. (B) Blot analyses of biotinylated, soluble Muc4–ErbB2 complex from the BEVS, using horseradish peroxidase–conjugated streptavidin. Soluble Muc4 and ErbB2 were expressed separately and analyzed in parallel to the complex.