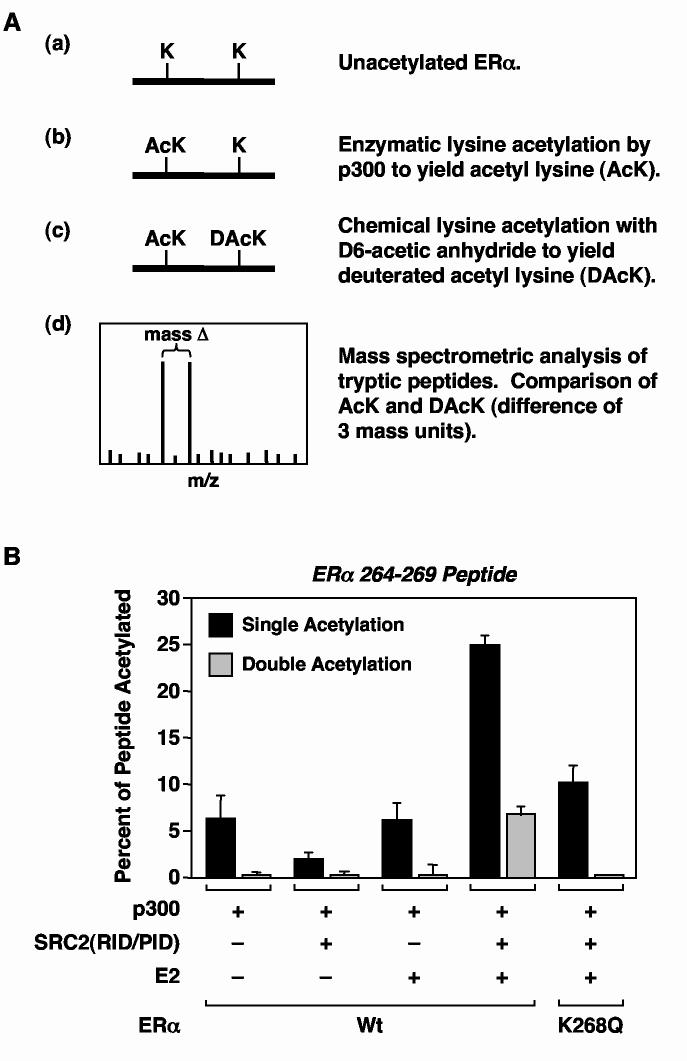
Fig. 4.
Quantitative mass spectrometric analysis of ERα acetylation by p300. (A) Schematic diagram of the quantitative mass spectrometric procedure for determining site-specific ERα acetylation levels. (B) Quantitative mass spectrometric determination of SRC- and E2-dependent acetylation by p300 of peptide 264-269 from trypsin-digested full-length wild type or K268Q mutant ERα. The ERαs were assayed for acetylation by p300 in the presence of GST-SRC2(RID/PID) and E2 as described for Fig. 1B and then subjected to quantitative MALDI-QqTOF spectrometry as described in (A). The data are expressed as amount of acetylated 264-269 peptide (i.e., AcK) relative to the total amount of 264-269 peptide in the reaction (i.e., AcK + DAcK). As indicated in Table 1, K268 is the major site (>95%) of single acetylation in the 264-269 peptide. In the K268Q mutant, all of the acetylation of the 264-269 peptide is at K266.