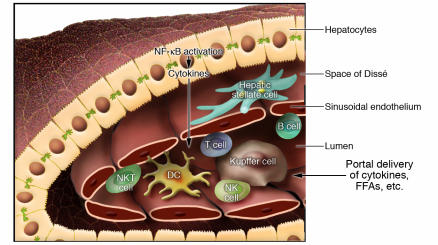
Figure 3. Potential mechanisms for adiposity-induced inflammation in the liver.
Healthy liver contains a broad repertoire of cells that participate in inflammatory and immune responses, including resident hepatic macrophages (Kupffer cells), B and T cells, NK and NKT cells, DCs, liver sinusoidal endothelial cells, hepatic stellate cells, and hepatocytes. Hepatic steatosis and obesity are accompanied by the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways in liver. Proinflammatory cytokines and FFAs, produced either by hepatocytes in response to steatosis or by abdominal fat tissue, may activate Kupffer cells. Numbers of regulatory NKT cells decrease in parallel with the Kupffer cell activation.