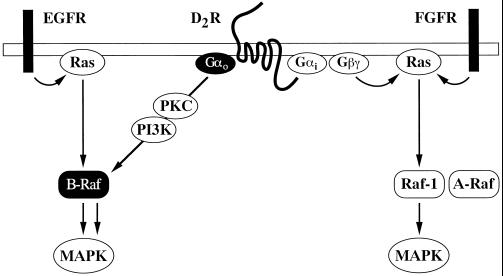
Figure 9.
Model of signaling pathways regulating Raf and MAPK in CHO cells. The EGF receptor (EGFR) activates Ras and B-Raf, whereas the FGF receptor (FGFR) activates Ras, Raf-1, and A-Raf. Activated Gαo potentiates MAPK activation by Ras and EGFR but not FGFR. The G protein subunit stimulates the kinase activity of B-Raf by a Ras-independent and PKC- and PI3K-dependent mechanism, which is insufficient to promote MAPK activation. It is proposed that this mechanism can efficiently stimulate the MAPK pathway in the presence of a B-Raf-activating signal from Ras or the EGFR. The dopaminergic D2 receptor (D2R), which couples to both Gi and Go, appears to stimulate MAPK through Ras activation of Raf-1. This effect is presumably mediated by G protein βγ complexes and, possibly, Gαi subunits. Upon stimulation of this receptor, the Ras-independent and PKC- and PI3K-dependent activation of B-Raf induced by Gαo does not produce a MAPK response.